�����
������������ �������
SK
SERIES
��������� MITSUBISHI S4K ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4K ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4K-T ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4K-T ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S6K ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S6K-T ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S6K-Y2DT31 ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S6K-Y2DT31 ���������� �� �������
SE
SERIES
��������� MITSUBISHI S2E ���������� �� ������������ � ������������
��������� MITSUBISHI S2E ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S2E2 ���������� �� ������������ � ������������
��������� MITSUBISHI S2E2 ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3E ���������� �� ������������ � ������������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3E ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3E2 ���������� �� ������������ � ������������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3E2 ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4E ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4E ���������� �� ������������ � ������������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4E ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4E2 ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4E2 ���������� �� ������������ � ������������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4E2 ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4E2-T ���������� �� ������������ � ������������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4E2-T ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S6E ���������� �� ������������ � ������������
��������� MITSUBISHI S6E ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S6E2 ���������� �� ������������ � ������������
��������� MITSUBISHI S6E2 ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S6E2-T ���������� �� �������
SF
SERIES
��������� MITSUBISHI S3F ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4F ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4F-T ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S6F ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S6F-T ���������� �� �������
SL
SERIES
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L-31FS ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L-62AG2 ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L-62APH2 ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L-W261TM ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L-Y161DPH ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L ���������� �� ������������ � ������������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L-T ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2 ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2-31FS ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2-31FSA ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2-61ES ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2-61SD ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2-61SDH ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2-61ST ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2-61WH ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2-62AG2 ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2-62APH ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2-62APH2 ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2-63ES ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2-63SGM ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2-E331AC ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2-V363JG ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2-W262SD ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2-Y161DPH ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2-Y162ST ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2-Y261TM ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2-Z261SDH ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2 ���������� �� ������������ � ������������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2 ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S3L2-T ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L-61DM ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L-61KL ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L-61ST ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L-62AG2 ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L-62APH ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L-62APH2 ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L-65DM ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L-W161DG ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L-Y161DPH ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L-Y162KL ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L-Y162ST ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L-Y1T62ST ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L-Y261TM ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L ���������� �� ������������ � ������������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L-T31FS ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L-T61ST ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L-T ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2 ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-31FS ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-61DM ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-61ES ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-61KL ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-61SD ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-61SDH ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-61WH ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-62AG2 ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-62APH2 ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-63ES ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-63SGM ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-65DM ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-V363JG ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-Y161DG ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-Y161DPH ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-Y161SD ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-Y162KL ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-Y162WM ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-Y261TM ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-Y262SD ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-Z261SDH ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2 ���������� �� ������������ � ������������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2 ���������� �� �������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-T61DM ������� �������� ������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-T ���������� �� ������������ � ������������
��������� MITSUBISHI S4L2-T ���������� �� �������
Download or browse on-line these Service Manual for Mitsubishi S4S Engine.
Summary of Contents:
 |
[Page 1] Mitsubishi S4S SERVICE MANUAL MITSUBISHI DIESEL ENGINES S4S ses March 2002 J.. !!!!I’D’!S~~!~!. |
 |
[Page 2] Mitsubishi S4S … |
 |
[Page 3] Mitsubishi S4S Foreword This service manual is written to familiarize you with the maintenance of your S4S and S6S Diesel Engine. If the engine is carefully maintained it will deliver a long productive life and efficient performance marked by power and economy. Bef… |
 |
[Page 4] Mitsubishi S4S Notes, Cautions, Warnings, Dangers Notes, cautions, wamings, dangers are used in this manual to emphasize important or critical instructions or advice. (&OANGER) &WARNING (&CAUTION) (NOTE) ‘Ierms Used in This Manual Indicates the mos… |
 |
[Page 5] Mitsubishi S4S Summary of Manual Contents Group 1. General 2. Maintenance Standards 3. Special Tools 4. Overhaul Instructions 5. Adjustments, Bench Test, Performance Tests 6. Engine Auxiliaries Removal and Installation 7. Engine Main Parts 8. Inlet and Exhaust Syst… |
 |
[Page 6] Mitsubishi S4S … |
 |
[Page 7] Mitsubishi S4S GENERAL 1. Outline 1- 2 1.1 External View 1- 2 1.2 Engine Serial Number Location 1- 6 1.3 Engine Model and Application Codes 1- 6 2. Specifications 1- 7 3. Tips on Disassembly and Reassemb1y 1-13 3.1 Disassembly 1-13 3.2 Reassembly 1-13 Di |
 |
[Page 8] Mitsubishi S4S GENERAL 1. Outline 1.1 External View [848 — Standard] Fuel filter Fuel injection pump Fan IFront I Fuel feed pump C’-I) n Inlet manifold Fuel injection nozzle ETR stop solenoid Governor Coolant drain plug Dipstick I Rear I <>-tt-++—Flywhe… |
 |
[Page 9] Mitsubishi S4S GENERAL [S4S-DT — Standard] IRear I ::n » .’ (I~I\ Fuel injection pump n Fuel filter \ <, I/In, let manifold h—.rT,—-1JI Fuel injection nozzle Fan ~ rr-. ~ tJUI fT»i»T»i: ~ r~~ ~?n’\~ I hl vETRstopsolenoid Water pu… |
 |
[Page 10] Mitsubishi S4S GENERAL [868 — Standard] uel filter Fuel injection pump lnlet manifold I Rear I Flywheel Oil filter Dipstick Governor t:~~~ah~~::~~r Coolant drain plug Oil drain plug %~-1—-le:::::~I-~e:::::~~—:v: Fuel injection nozzle 1NI»bb!l;a ETR stop sol… |
 |
[Page 11] Mitsubishi S4S GENERAL [S6S-DT — Standard] Fan Water pump IFront I Gil filler Exhaust manifold I Rea.. I Starter Fuel injection nozzle ETR stop solenoid ).F~~~~~~ Governor I Rear I Flywheel Gil drain plug Dipstick ILef! view I Turbocharger Thermostat Alternator IFr… |
 |
[Page 12] Mitsubishi S4S GENERAL 1.2 Engine Serlal Number Location The engine serial number is located on the side of the crankcase. 1.3 Engine Model and Application Codes s D s — [Q][ïJ ~ 1-6 T : Equipped with turbocharger D : Direct injection type Series code Number of cy… |
 |
[Page 13] Mitsubishi S4S 2. Specifieations GENERAL Model designation S4S S4S-DT Type Water-cooled, 4-stroke cycle No. of cylinders — arrangement 4- in line Combustion chamber type Swirl chamber Direct injection Valve mechanism Overhead Cylinder bore x stroke mm[in.] 94 x 120… |
 |
[Page 14] Mitsubishi S4S GENERAL Model designation S4S S4S-DT Refill capacity (engine water jacket) 5.5 [1.5] 5 [1.3] liter [U.S. gal.] Type Centrifugal Water pump Speedrationto crankshaft 1.3 Ei Capacity 160 [42.3] at 0.075 MPa [0.75 kgf/cm’] discharge pressure 2 liter… |
 |
[Page 15] Mitsubishi S4S GENERAL Model designation S4S I S4S-DT Type 3-phase, with rectifier Output V-A 12-50 Working speed min:’ 1000 to 18000 Altemator Rated output generating 5000 Ei speed min:’ s <IJ Maximum perrnissib1e>-. 22000 co C;; speed min:’ o… |
 |
[Page 16] Mitsubishi S4S GENERAL Model designation S6S S6S-DT Type Water-cooled, 4-stroke cycle No. of cylinders — arrangement 6-in line Combustion chamber type Swirl chamber Direct injection Valve mechanism Overhead Cylinder bore x stroke mm [in.] 94 x 120 [3.70 x 4.72] Pis… |
 |
[Page 17] Mitsubishi S4S GENERAL Model designation S6S S6S-DT Refill capacity (engine water jacket) 9 [2.4] 8 [2.1] liter [U.S. gal.] Type Centrifugal Water pump Speedrationto crankshaft 1.3 Ei Capacity 160 [42.3] at 0.075 MPa [0.75 kgf/cm»] discharge pressure B liter [… |
 |
[Page 18] Mitsubishi S4S GENERAL Model designation S6S I S6S-DT Type 3-phase, with rectifier Output V-A 12 -50 Working speed min-I 1000 to 18000 a Altemator Rated output generating 5000 B speed min-I ‘» >. Maximum permissible ‘» 22000 ‘<‘J… |
 |
[Page 19] Mitsubishi S4S 3. Tips on Disassembly and Reassembly This service manual covers recommended procedures to be followed when servicing diesel engines. It also contains information on special tools required and basic safety precautions. It is the responsibility of ser… |
 |
[Page 20] Mitsubishi S4S … |
 |
[Page 21] Mitsubishi S4S MAINTENANCE STANDARDS 1. Maintenance Standards Table 2- 2 2. Tightening Torques , 2- 9 2.1 Important Bolts and Nuts 2- 9 2.2 Standard Bolts 2-10 2.3 Standard Studs 2-10 2.4 Standard Plugs .. 2-10 3. Sealants and Lubricants Table 2-11 |
 |
[Page 22] Mitsubishi S4S MAINTENANCE STANDARDS 1. Maintenance Standards Table Unit: mm [in.] Nominal Assembly Standard Repair Service Group Inspeetion Point Limit Limit Remark Value (Standard Clearance) (Clearance) (Clearance) Maximum min-I, (no-load) According to engine Adj… |
 |
[Page 23] Mitsubishi S4S MAINTENANCE STANDARDS Unit: mm [in.] Nominal Assembly Standard Repair Service Group Inspeetion Point Limit Limit Remark Value (Standard Clearance) (Clearance) (Clearance) ~ 14.000 to 14.018 14.100 … Inside diameter 0 ..0 [0.5512 to 0.5519] [0.5551]… |
 |
[Page 24] Mitsubishi S4S MAINTENANCE 8TANDARD8 Unit: mm [in.] Nominal Assembly Standard Repair Service Group Inspeetion Point Limit Limit Remark Value (Standard Clearance) (Clearance) (Clearance) Inside diameter of 19.010 to 19.030 S rocker bushing 19 [0.7484 to 0.7492] &quo… |
 |
[Page 25] Mitsubishi S4S MAINTENANCE STANDARDS Unit: mm [in.] Graup Inspeetion Point Repair Service Nominal Assembly Standard Limit Limit Value (StandardClearance) (Clearance) (Clearance) Remark 1.50 [0.0591] (0.200) ([0.0079]) (0.150) ([0.0059]) (0.150) ([0.0059]) 0.30 to 0… |
 |
[Page 26] Mitsubishi S4S MAINTENANCE STANDARDS Unit:mm [in.] Nominal Assembly Standard Repair Service Group Inspeetion Point Limit Limit Remark Value (Standard Clearance) (Clearance) (Clearance) Clearance between (0.009 to 0.050) (0.100) Replace bushing. shaft and bushing ([… |
 |
[Page 27] Mitsubishi S4S MAINTENANCE STANDARDS Unit: mrn [in.] Nominal Assembly Standard Repair Service Group Inspeetion Point Limit Limit Remark Value (Standard Clearance) (Clearance) (Clearance) 17.65 18.14 to 19.12 Make shirn adjustrnent. DI (180) (l85 to 195) Pressure va… |
 |
[Page 28] Mitsubishi S4S MAINTENANCE 8TANDARD8 Unit: mm [in.] Nominal Assembly Standard Repair Service Group Inspeetion Point Limit Limit Remark Value (Standard Clearance) (Clearance) (Clearance) Diameter of 38.7 38.1 commutator [1.S2] [I.SO] Runout of 0.03 0.1 commutator [0… |
 |
[Page 29] Mitsubishi S4S 2. Tightening Torques 2.1 Important Bolts and Nuts MAINTENANCE 8TANDARD8 Thread Width Tightening Torque Description Dia. x Pitch across flats, Remark (M-thread) mm N·m kgf-rn IbHt Cylinder head M12 x 1.75 19 113 to 123 11.5 ta 12.5 83 ta 90 Rocker c… |
 |
[Page 30] Mitsubishi S4S MAINTENANCE STANDAROS Thread Width Tightening Torque Description Dia. x Pitch across flats, Remark (M-thread) mm N·m kgf-m lbf-ft Overheat warning unit M16 x 1.5 19 20.6 to 24.5 2.1 to 2.5 15.2 to 18.1 (thermostat) Starter terminal B M8 x 1.25 12 9…. |
 |
[Page 31] Mitsubishi S4S 3. Sealants and Lubricants Table MAINTENANCE STANDARDS Apply to Mating part Sealant or Lubricant How to Use üil pan Crankcase Three Bond 12Ü?C Apply to seal. Rear bearing cap Rear bearing cap Three Bond 1212 Apply to corners befare seat on crankcas… |
 |
[Page 32] Mitsubishi S4S … |
 |
[Page 33] Mitsubishi S4S SPECIAL rOOlS Special TooI List 3-2 |
 |
[Page 34] Mitsubishi S4S SPECIAL TOOLS Special Tooi List Taal name Valve spring pusher Valve guide remave Valve guide installer Stem seal installer Valve seat insert caulking taal Piston ring pliers Part No. 30691—04500 32A91—o0300 3 2A91—o0 100 32A91-10200 Inlet valve: 3… |
 |
[Page 35] Mitsubishi S4S SPECIAL TOOLS Tooi name Part No. Shape Use Oil seal sleeve installer 30691-13010 set Crankshaft rear oil seal sleeve installation Engine tuming Compression pressure measurement Compression pressure measurement Compression pressure measurement 58309-7… |
 |
[Page 36] Mitsubishi S4S … |
 |
[Page 37] Mitsubishi S4S OVERHAUL INSTRUCTIONS 1. Determination of Overhaul Timing 4-2 2. Testing the Compression Pressure 4-3 |
 |
[Page 38] Mitsubishi S4S OVERHAUL INSTRUCTIONS 1. Determlnation of Overhaul Timing In most cases the engine should be overhauled when the engine’s compression pressure is low. Other factors that indicate the necessity of engine overhaul are as follows: (a) Decreased pow… |
 |
[Page 39] Mitsubishi S4S 2. Testlag the Compression Pressure (1) Remove the injection nozzle from the cylinder head where the compression pressure is to be measured. (2) On the direction injection type engine, attached gage adaptor (32A9l-01100) to the cylinder,and conneet t… |
 |
[Page 40] Mitsubishi S4S OVERHAUL INSTRUCTIONS ……——-i[&CAUTION JI——-. (a) Measure the compression pressure at regular intervals to obtain correct data. (b) The compression pressure will be slightly higher ina new or overhauled engine due to new piston rings, … |
 |
[Page 41] Mitsubishi S4S ADJUSTMENTS, BENCH TEST, PERFORMANCE TESTS 1. Adjustments 5- 2 1.1 Valve Clearance 5- 2 1.2 Fuel System Bleeding 5- 3 1.3 Fuel Injection Timing 5- 4 1.4 No-load Minimum (Idling) Speed and Maximum Speed Setting 5- 5 1.5 V-belt Inspeetion and Adjustmen… |
 |
[Page 42] Mitsubishi S4S ADJUSTMENTS, BENCH TEST, PERFORMANCE TESTS 1. Adjustments 1.1 ValveClearance Valve clearance should be inspected and adjusted when the engine is cold. Unit: mm [in.] Item Assembly Standard Valve clearance InIet 0.25 [0.0098] (cold setting) Exhaust (l… |
 |
[Page 43] Mitsubishi S4S (2) Adjusting (a) Loosen the loek nut of the adjusting screw. Adjust the clearance by tuming the screw in either direction to the extent that the gage is slightly gripped between the rocker arm and valve cap. (b) After adjusting the clearance, tighte… |
 |
[Page 44] Mitsubishi S4S ADJUSTMENTS, BENCH TEST, PERFORMANCE TESTS 1.3 Fuel Injection Timing The injection timing varies according to the output, speed and specifications of the engine. Be sure to verify the timing by referring to the specifications. (1) Bringing the No.l c… |
 |
[Page 45] Mitsubishi S4S (3) Adjusting injecting timing (a) If the injection timing is retarded, move the injection pump toward the crankcase. If the timing is advanced, move the pump away from the crankcase. (b) One graduation of the scale on the injection pump coupling cha… |
 |
[Page 46] Mitsubishi S4S ADJUSTMENTS, BENCH TEST, PERFORMANCE TESTS (1) Starting engine (a) Pull speedcontrollevertothe high speed side. Operate the starter switch to crank the engine. (b) The engine will fire up at 150 min-lof cranking speed. When the engine fires, hold the… |
 |
[Page 47] Mitsubishi S4S (3) Setting rack (maximum output) (a) Hold the speed controllever at the position for the indicated output and speed. (b) Under this condition, check to be sure that the engine is running in a steady state. (c) With the engine running in a steady sta… |
 |
[Page 48] Mitsubishi S4S ADJUSTMENTS, BENCH TEST, PERFORMANCE TESTS (5) Deterrnining speed regulation (speed droop) [I] Speed regulation upon removing load (a) Run the engine with the speed control lever set at the position for the rated load and speed. (b) Vnder this condit… |
 |
[Page 49] Mitsubishi S4S (6) Setting no-load maximum speed (make governor notch adjustment) (a) This adjustment is to be made by turning the adjustingscrew for the swivelleverto increase ordecrease the preload of the govemor spring. (b) To gain access to the adjusting screw,… |
 |
[Page 50] Mitsubishi S4S ADJUSTMENTS, BENCH TEST, PERFORMANCE TESTS 1.5 V-belt Inspeetion and Adjustment Push the belt inward with thumb pressure exerted midway between the pulleys, as shown, to check the belt tension (deflection). If the tension is incorrect, loosen the adj… |
 |
[Page 51] Mitsubishi S4S 2. Bench Testing An overhauled engine should be tested for performance on a dynamometer. This test is also for breaking in the major running parts of the engine. To test the engine, follow the procedures described below: 2.1 Starting Up (l) Inspeet t… |
 |
[Page 52] Mitsubishi S4S ADJUSTMENTS, BENCH TEST, PERFORMANCE TESTS 3. Performance Tests There are various performance test procedures, and here the procedures for «Earth moving machinery Engines, Part 1 : Test code of net power (JIS D 0006-1)» and «Earth movi… |
 |
[Page 53] Mitsubishi S4S ADJUSTMENTS, BENCH TEST, PERFORMANCE TESTS (2) Calculation of corrected power Multiply the measured brake power or torque by the calculated diesel engine correction factor (see below) to obtained a corrected value. Corrected output =Correction factor… |
 |
[Page 54] Mitsubishi S4S … |
 |
[Page 55] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE AUXlllARIES REMOVAl AND INSTAllATION 1. Preparation 6- 2 2. Engine Auxiliaries Removal 6- 2 3. Engine Auxiliaries Installation 6- 7 |
 |
[Page 56] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE AUXILIARIE8 REMOVAL AND IN8TALLATION This section explains the procedures and tips for removal and installation of the auxiliaries — the pre1iminary process to go through for overhauling the engine. 1. Preparation (a) Shut off the fue1 supply,… |
 |
[Page 57] Mitsubishi S4S Return pipe (2) Exhaust manifold Remove the bolts that hold exhaust manifold to the cylinder head. Remove the manifold and gasket from the head. (3) Fuel filter (a) Disconneet fuel pipes and from the fuel filter. (b) Remove fuel filter complete with … |
 |
[Page 58] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE AUXILIARIE8 REMOVALAND IN8TALLATION (6) Fuel injection nozzles (direct injection type) Remove gland, then remove nozzle and gasket from the cylinder head. (7) Fuel injection nozzles (swirl chamber type) Remove nozzle and gasket. (8) Glow plugs… |
 |
[Page 59] Mitsubishi S4S (10) Fuel injection pump (a) Remove oil pipe. (b) Remove bolts that hold the gear case cover. (c) Remove bolts that hold the flange plate. Remove pump with gear and flange from the front plate. (Some engines are not equipped with pump bracket.) (11) … |
 |
[Page 60] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINEAUXILIARIE8 REMOVALAND IN8TALLATION (14) Water pump (a) Remove the bolts that holdfan and pulley and remove them. (b) Remove the bolts that hold water pump and remove the pump and gaskets. (15) Starter Disconneet harness from starter. Remove nu… |
 |
[Page 61] Mitsubishi S4S 3. Engine Auxiliaries Installation To install the engine auxiliaries, follow the removal procedures in reverse. After installation, service them as follows: (a) Refill the engine with the recommended oil up to the specified level. (b) Refill the cool… |
 |
[Page 62] Mitsubishi S4S … |
 |
[Page 63] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE MAIN PARTS 1. Cylinder Heads and ValveMechanism 00.0000.00000000.0000000000.000000.00.0000.0000000000.0000.0000.00′.000000.00″000000. 7- 2 1.1 Disassembly .00 00 •••••••••••••••••••••••�… |
 |
[Page 64] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE MAIN PARTS 1. Cylinder Head and Valve Mechanism 1.1 Disassembly Check valve cap contact face for wear. Check oil hole for clogging. Check for cracks. or’carbon or scale deposits, Check face for pitring or ridging (exhaust valve), Check st… |
 |
[Page 65] Mitsubishi S4S (1) Removing rocker shaft assembly (a) Loosen the adjusting screw one rotation. (b) Loosen the bolts, short and long, that hold the rocker shaft bracket to the cylinder head. Be sure to loosen the short bolt first. Remove the rocker shaft assembly fr… |
 |
[Page 66] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE MAIN PARTS (4) Remove valve and valve spring (a) Use valve spring pusher (30691-04500) to compress the valve spring, then remove the valve cotters. (b) Remove the valves and valve springs. ,…..——-I[ NOTE ÎI- -, If the original valves ar… |
 |
[Page 67] Mitsubishi S4S Valves, valve guldes and valve seats (1) Measuring valve stem Measure the diameter of the valve stem as shown in the illustration. If the stem is wom beyond the service limit or unevenly wom excessively, replace the valve. Unit: mm [in.] Item Nominal… |
 |
[Page 68] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE MAIN PARTS (b) To install areplacement guide, use valve guide installer (32A91-o0100). Press Valve guide instalIer …..———iLLCAUTION 1——-, The installation depth for the valve guide is specified; be sure to use the valve guide instal… |
 |
[Page 69] Mitsubishi S4S (5) Refacing valve face If the valve face is badly wom, reface it with a valve refacer. NOTE 1———, a) Set a valve refacer to an angle of 30° b) The valve has a stellate facing. This facing will be gone if the valve margin exceeds the service l… |
 |
[Page 70] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE MAIN PARTS (b) Before installing replacement valve seats in the cylinder head, measure the bores in the cylinder head for the valve seats. (c) Chill the valve seat in liquid nitrogen of — l70 DC [-274 DF] for more than 4 minutes with the cylin… |
 |
[Page 71] Mitsubishi S4S (b) Using lapping tool, hold the valve against the seat and rotate it only a part of a turn, then raise the valve off the seat, rotating it to a new position. Then press the valve against the seat for another part of aturn. Repeat this operation unti… |
 |
[Page 72] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE MAIN PARTS (10) Measuring cylinder head warpage Using a heavy accurate straight edge and feeler gages, check the gasket contact surface for warpage in two positions lengthwise, two crosswise and two widthwise as shown in the illustration. If t… |
 |
[Page 73] Mitsubishi S4S (2) Installing valve and valve spring (a) Put the valve spring and retainer on the valve guide. Using valve spring pusher (30691- 04500), compress the valve spring and install the valve cotters. (b) Tap the valve stem top with a soft-faeed hammer sev… |
 |
[Page 74] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE MAIN PARTS No. of bolts: 25 Cylinder head bolt tightening sequence (565) (4) Reassembling rocker shafts Af ter reassembling the rocker shafts, make sure the rocker arms move smoothly. Reassembling rocker shafts (a) Install the valve caps in po… |
 |
[Page 75] Mitsubishi S4S 2. Flywheel 2.1 Disassembly Replace gasket. Checks for cracks or defective dowel hole. I Disassembly sequence I CD Flywheel Check for wom or defective lip. Check for cracks or defective dowel hole. Check ring gear for wom or detective teeth. Remove �… |
 |
[Page 76] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINEMAIN PARTS (1) Removing flywheel (a) Remove one ofthe bolts that hold theflywheel to the crankshaft. (b) Run safety bar (M12 x 1.25) in the holefrom which the bolt was removed in Step (a). Remove the remaining flywheel bolts. (c) Remove the fly… |
 |
[Page 77] Mitsubishi S4S (2) Face runout and circular runout (radial eccentricity) of flywheel Set a dia! indicator at the friction(vertical) surface and turn the flywheel one full revolution to check the face run out. Set a dial indicator at the horizontal surface of the pi… |
 |
[Page 78] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE MAIN PARTS 2.3 Reassembly (1) Installing oil seal (According to engine specification) Apply a thin coat of grease to the oil seal and install the oil seal to the flywheel housing with an installer. ..——-1 NOTE 1———, If the oil seal c… |
 |
[Page 79] Mitsubishi S4S 3. Damper, Timing Gears and Camshaft 3.1 Disassembly ENGINE MAIN PARTS Replace gasket Check for wear or damage. Check teeth for wear, nicks, burrs or chips. Check keyway apçl bushing for damage or wear. Check for we:n» Check for stripped thread… |
 |
[Page 80] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE MAIN PARTS (I) Removing damper (S6SIDT) (a) Install two safety bars (MI2 x 1.25) in the rear end of the crankshaft to hold the crankshaft. (b) Remove the damper. llliWARNING Be to install the safety bars securely. (2) Removing crankshaft pulle… |
 |
[Page 81] Mitsubishi S4S (6) Removing oil pump gear Loosen the nut and remove the gear. (7) Removing idler gear Remove the thrust plate and remove the gear as shown. (8) Removing camshaft (a) Turn the crankcase upside down. (b) Position the camshaft gear so that its lighteni… |
 |
[Page 82] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINEMAIN PARTS (9) Removing camshaft gear Remove the gear from the camshaft with a puller. Now the thrust plate can be removed. r——-1( NOTE 11- —, Do not remove the camshaft gear and thrust plate unless they are damagedto the extent of requir… |
 |
[Page 83] Mitsubishi S4S 3.2 Inspeetion Camshaft and camshaft bushlngs (1) Measuring camshaft end play Measure the camshaft end play as shown in the illustration. If the end play exceeds the service limit, replace the thrust plate. Unit: mm [in.] Item Assembly Service Standa… |
 |
[Page 84] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE MAIN PARTS (3) Measuring camshaft deflection Support the camshaft on its front and rear journals in V-blocks. With the dia! indicator set at 0.00 mm [0.0000 in.] at the center joumal, turn the camshaft full one revolution and read the indicato… |
 |
[Page 85] Mitsubishi S4S (5) Replacing camshaft bushings (a) Ifthe clearancebetween the camshaftjoumal and bore in the crankcase exceeds the service limit, refinish the bore to 57H6 («‘8019) 3.125 Ra. and install bushings. (c) To replace or install bushings, use ca… |
 |
[Page 86] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINEMAIN PARTS (2) Measuring clearance between idler gear bushing and shaft Measure the inside diameter of the bushing and the diameter of the shaft to determine the clearance between the two. If the clearance exceeds the service limit, replace the… |
 |
[Page 87] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE MAIN PARTS (1) Installing front plate 3.3 Reassembly (b) Tighten the bolts that hold the front plate to the crankcase to the specified torque. Installing front plate 10.0 to 13.0 N·m (1.0 to 1.3 kgf-m) [7.23 to 9.40 lbf-ft] Tightening torque … |
 |
[Page 88] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE MAIN PARTS (4) Installing idler gear (b) Tighten the thrust plate mounting bolts to the specified torque. (a) Install the idler gear by aligning its matching mark with those on the crankshaft gear, injection pump gear and camshaft gear and ins… |
 |
[Page 89] Mitsubishi S4S (7) Inspecting valve timing It is not necessary to inspeet the valve timing, provided that all match marks on the timing gears are aligned. Inspeetthe timing for verification as explained below: (a) Using a 3 mm [0.12 in.] thick smooth steel plate, a… |
 |
[Page 90] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE MAIN PARTS (8) Installing oil seal (if necessary) Apply a small amount of grease to the oil seal and install it to the timing gear case with an installer. Installingoil seal (b) Apply oil to the lip of the oil seal. (9) Installing timing gear … |
 |
[Page 91] Mitsubishi S4S .———1 NOrf ‘1— —, To squeeze out a4 mm [0.2 in.] thickness ofThree Bond, cut the first node of the nozzie. ENGINE MAIN PARTS Nozzle for Three Bond 12Ü7Ctube (11) Installing crankshaft pulley Install two safety bars (MI2 x 1.25) to the … |
 |
[Page 92] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE MAIN PARTS . 4. Pistons, Connecting Rods, Crankshaft, Crankcase and Tappets 4.1 Disassembly Check for scratching, pitting, flaking. chipping or loss of overlay. NOTE: When replacing the crankcase, carefully rernove the components (such as an o… |
 |
[Page 93] Mitsubishi S4S (l) Removing connecting rod cap (a) Remove the nuts that hold the cap to the connecting rod. Tap the bolts squarely and evenly with a hammer and, after the cap comes off the reamer bolts, remove the cap. (b) Mark the bearings for cylinder number and … |
 |
[Page 94] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE MAIN PARTS (5) Removing piston pin Using snap ring pliers, remove the snap rings from the piston. Remove the piston pin to separatethe piston from the connecting rad. If it is difficult to pull out the pin, heat the piston with a piston heater… |
 |
[Page 95] Mitsubishi S4S 4.2 Inspeetion Crankcase (1) Gasket contact surface Measure flatness of the gasket contact (top) surface with a heavy accurate straight edge and feeler gages, in three positions lengthwise, two crosswise and two widthwise, as shown in the illustratio… |
 |
[Page 96] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE MAIN PARTS (d) If any cylinder is unevenly worn, determine the oversizeon the basis of the maximum wear noted to ensure perfect roundness in the oversized bore. ..———-J[ NOrE JI———-.., (a) Refinish all cylinders to the same oversiz… |
 |
[Page 97] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE MAIN PARTS WEIGHTmark FRONTmark (2) Measuring cut clearance between ends of piston ring Put the piston ring in the gage or a new cylinder sleeve and measure the cut clearance with feeler gages as shown in the illustration. Ifthe clearance exce… |
 |
[Page 98] Mitsubishi S4S ENGINE MAIN PARTS (3) Measuring clearance between groove and piston ring Put a new piston ring in the groove. Measure the clearance between the groove and piston ring with a straight edge and feeler gages as shown in the illustration. If the clearanc… |
 |
[Page 99] Mitsubishi S4S (5) Measuring piston protrusion If the piston protrusion is not correct, check the various parts for clearance. Measure the piston protrusion as outlined below. (a) Measure the top dead center of the pistons with a dial gage. (b) Install the dial ind… |
 |
[Page 100] Mitsubishi S4S Measuring connecting rad bearing ENGINE MAIN PARTS Connecting rods, conneetion rod hearings and piston pin bushings (1) Clearance between connecting rod bearing and crankpin Measure the diameter of the crankpin and the inside diameter of the connecti… |
Только оригинальные руководства
Доступно сразу после оплаты
Полное соответствие бумажным изданиям
100% защита ваших оплат
Издательство: © «Motorist»
ISBN: 977-129-542-358-5
Количество страниц: 241
Формат: файл PDF
О руководстве
Тип двигателя: Mitsubishi S4S / S6S
В руководстве вы найдете
- Пошаговое руководство по ремонту различных узлов и агрегатов
- Инструкцию по самостоятельному уходу и обслуживанию
- Сведения о конструкции двигателя и о том как предупредить неисправность
- Информацию для поездки на СТО, если самостоятельный ремонт невозможен
Содержание
Меры предосторожности
Общие сведения
- Структура
- Технические характеристики
- Советы по разборке и сборке
Стандарты технического обслуживания
- Таблица стандартов технического обслуживания
- Таблица моментов затяжки
- Таблица герметиков и смазочных материалов
Специальные инструменты
Инструкции по капитальному ремонту
- Определение сроков капитального ремонта
- Проверка давления сжатия
Подготовка к разборке
Разборка основных частей двигателя
- Головка блока цилиндров и клапанный механизм
- Маховик
- Демпфер, зубчатые колеса и распределительный вал
- Поршни, шатуны, коленчатый вал и картер
Осмотр и ремонт основных частей двигателя
- Головка блока цилиндров и клапан
- Маховик, распределительный вал и ГРМ
- Картер, поршни, шатуны, коленчатый вал и толкатели
Сборка основных деталей двигателя
- Картер, толкатели, коленчатый вал, поршни и шатуны
- Механизмы синхронизации
- Маховик
- Головка блока цилиндров и клапанные механизмы
Снятие топливной системы
- Топливный фильтр и топливопроводы
- Трубки впрыска топлива, трубки утечки топлива и форсунки впрыска топлива
- ТНВД
Разборка, осмотр и сборка топливной системы
- Топливный фильтр
- Форсунки впрыска топлива
Снятие системы смазки
- Масляный фильтр и предохранительный клапан
- Масляный радиатор
- Масляный насос, масляный поддон и масляный фильтр
Разборка, осмотр и повторная сборка системы смазки
- Масляный насос
- Масляный радиатор
- Масляный фильтр
- Перепускной клапан
- Предохранительный клапан
Установка системы смазки
- Масляный насос, масляный поддон и масляный фильтр
- Масляный радиатор
- Масляный фильтр и предохранительный клапан
Снятие системы охлаждения
- Вентилятор охлаждения, шкив вентилятора и клиновой ремень
- Термостат
- Водяной насос
Разборка, проверка и сборка системы охлаждения
- Термостат
- Водяной насос
Установка системы охлаждения
- Водяной насос
- Термостат
- Вентилятор. Шкив вентилятора и клиновой ремень
Снятие впускной и выпускной систем
- Турбокомпрессор
- Впускной коллектор
- Выпускной коллектор
Разборка, проверка и повторная сборка впускной и выпускной систем
- Впускной и выпускной коллекторы
Монтаж впускной и выпускной систем
- Выпускной коллектор
- Впускной коллектор
- Турбокомпрессор
Снятие электрооборудования
- Стартер
- Генератор
- Свеча накаливания
Разборка, проверка и повторная сборка электрооборудования
- Стартер
- Генератор
- Магнитный клапан (остановочный соленоид)
- Свеча накаливания
Установка электрооборудования
- Свеча накаливания
- Генератор
- Стартер
Проверка, регулировка, обкатка и эксплуатационные испытания
- Регулировка двигателя
- Обкатка двигателя
- Эксплуатационные испытания
Другое
- Разборка и сборка деталей общего назначения
Написать отзыв
Ваше Имя:
Ваш отзыв:
Оценка:
Отзывы покупателей
Нет отзывов об этом товаре.
FOREWORD
This service manual describes the specifications as well as the maintenance and adjustment procedures for Mitsubishi diesel engines. This manual also includes the detailed information on basic and special tools as the need arises.
The Mitsubishi diesel engines can offer highly efficient and reliable performance for many years to come, which, however, only can be achieved through the proper handling and the periodical inspection/maintenance work exercised in according to the procedures of disassembly, inspection/adjustment and reassembly described in this manual.
Before attempting any work on your engine, thoroughly read this manual to familiarize with the engine and the required procedures of the work.
All information contained in this manual is based on the engine produced at the time of publication and is subject to change as the engine improved without notice.
Pub. No. 99619-12140

HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
This Service Manual describes the specifications of Mitsubishi diesel engines (land and standard applications) and relevant service standards, as well as the procedures for servicing the engines such as for disassembly, inspection, repair and reassembly. This manual is divided into Groups. Each Group covers a specific area of the engine.
The fuel injection pump, the governor and the turbocharger are handled in a separate manual.
Major contents of Groups are listed on the “General Contents” page. Detailed contents of each Group are listed on the first page of that Group.
For information on the operations and recommended inspection/maintenance schedule of forklift trucks, please refer to the operator’s manual for the forklift truck. For information on components/parts and spares ordering procedures, refer to the parts catalogue. For information on structures and functions, refer to appropriate training materials.
1. Notes on descriptions
(1)Parts shown in Figures as well as in the text are numbered in the order of disassembly.
(2)Inspecting points during disassembly are shown in the Disassembly figures by enclosing in the box.
(3)Service standards for inspection and repair are listed on the appropriate pages of this manual where the relevant descriptions are made. Also, a comprehensive listing of service standards is provided in Group 1.
(4)Parts reassembly sequence is provided below the Figure of that reassembly in the form of → → → →.
(5)In this manual, the following marks are provided to draw the reader’s attention to the safety notes described under the marks.



This indicates a potential danger in which property damage may result unless avoided.
Note: This stresses important points or provides useful tips on engine operations and service.
(6)Wherever hardware tightening requires the application of engine oil, “WET” is mentioned. If not mentioned, tighten the hardware “dry” (engine oil should not be applied).
2. Terms
Nominal value ······This is the nominal dimension of the part being measured.
Standard value ······This is the dimension of the individual part being measured, the clearance between the parts in question, or the standard performance in question. Standard values have been arranged within the range appropriate for the inspection being carried out, and are not necessarily the design values.
Limit ·····················Parts that have reached the limit value should be replaced or repaired whichever is appropriate.
3. Abbreviations and standards
BTDC = Before Top Dead Center
ATDC = After Top Dead CenterBBDC = Before Bottom Dead CenterABDC = After Bottom Dead CenterTIR = Total Indicator ReadingAPI = American Petroleum Institute
ASTM = American Society for Testing and MaterialsJIS = Japan Industrial Standards
LLC = Long Life CoolantMIL = Military Specifications
MSDS = Material Safety Data SheetsSAE = Society of Automotive Engineers
4. Units
Values shown in this manual are based on SI units (International System of Units). The corresponding metric values are shown in ( ) immediately after the SI values. The SI to metric conversions are based on the following.
Pressure: 1 MPa = 10.197 kgf/cm2Torque: 1 N m = 0.10197 kgf mForce: 1 N = 0.10197 kgf
Horsepower: 1 kW = 1.341 HP = 1.3596 PSMeter of mercury: 1 kPa = 0.7 cmHg
Meter of water: 1 kPa = 10.197 cmH2O (cmAq)Rotational speed: 1 min-1 = 1 rpm

GENERAL CONTENTS
|
Group No. |
Group Name |
Page |
|||
|
0 |
SAFETY CAUTIONS |
0 — 1 |
|||
|
GENERAL |
1 — 1 |
||||
|
SERVICE STANDARDS |
1 -11 |
||||
|
1 |
|||||
|
TOOLS LIST |
1 -21 |
||||
|
OVERHAUL TIMING |
1 -25 |
||||
|
REMOVAL PREPARATIONS |
1 -29 |
||||
|
ENGINE MAIN PARTS — DISASSEMBLY |
2 — 1 |
||||
|
2 |
Engine Main Parts |
ENGINE MAIN PARTS — INSPECTION AND |
2 -17 |
||
|
CORRECTION |
|||||
|
ENGINE MAIN PARTS — REASSEMBLY |
2 -33 |
||||
|
FUEL SYSTEM — REMOVAL |
3 — 1 |
||||
|
3 |
Fuel System |
FUEL SYSTEM — DISASSEMBLY, |
3 — 9 |
||
|
INSPECTION AND REASSEMBLY |
|||||
|
FUEL SYSTEM — INSTALLATION |
3 -25 |
||||
|
OIL SYSTEM — REMOVAL |
4 — 1 |
||||
|
4 |
Lubrication System |
OIL SYSTEM — DISASSEMBLY, |
4 — 5 |
||
|
INSPECTION AND REASSEMBLY |
|||||
|
OIL SYSTEM — INSTALLATION |
4 — 9 |
||||
|
COOLING SYSTEM — REMOVAL |
5 — 1 |
||||
|
5 |
Cooling System |
COOLING SYSTEM — DISASSEMBLY, |
5 — 5 |
||
|
INSPECTION AND REASSEMBLY |
|||||
|
COOLING SYSTEM — INSTALLATION |
5 — 9 |
||||
|
INLET AND EXHAUST SYSTEMS — |
6 — 1 |
||||
|
REMOVAL |
|||||
|
6 |
Inlet and Exhaust |
INLET AND EXHAUST SYSTEMS — |
|||
|
DISASSEMBLY, INSPECTION AND |
6 — 5 |
||||
|
Systems |
|||||
|
REASSEMBLY |
|||||
|
INLET AND EXHAUST SYSTEMS — |
6 — 7 |
||||
|
INSTALLATION |
|||||
|
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM — REMOVAL |
7 — 1 |
||||
|
7 |
Air starter System |
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM — DISASSEMBLY, |
7 — 7 |
||
|
INSPECTION AND REASSEMBLY |
|||||
|
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM — INSTALLATION |
7 -25 |
||||
|
Engine — |
ENGINE — INSPECTION / ADJUSTMENT |
8 — 1 |
|||
|
8 |
Inspection/Adjustment, |
||||
|
RUNNING-IN TRIAL |
8 -12 |
||||
|
Running-in Trial and |
|||||
|
Performance Test |
PERFORMANCE TEST |
8 -13 |
|||
|
9 |
Others |
DISASSEMBLY AND REASSEMBLY OF |
9 — 1 |
||
|
GENERAL PARTS |
|||||
|
Supplement |
|||||
|
Engine Inspection Sheets |

·····0-8
SAFETY CAUTIONS
Warning Risk of fire and explosion ···0-2
●Never use open fire ······························0-2
●Keep things tidy around the engine ··········0-2
●Do not open the crankcase until it has
cooled down········································0-2
●Pay attention to fuel and oil leakage ·········0-2
●Use explosion-proof light························0-2
●Prevent short circuit ······························0-2
●Keep fire extinguisher and first-aid kit
at hand ··············································0-2
Warning Risk of entanglement into
the machine························0-3
●Keep guards on the rotating parts ············0-3
●Ensure safety in the surrounding area
when starting the engine ························0-3
●Keep away from rotating parts while the engine is running··································0-3
●Lockout/tagout ·····································0-3
●Always stop the engine before any inspection/service·································0-3
●Remove the turning gear after use ···········0-3
Warning Risk of burn ························0-4
●Do not touch the engine while it is
running or for a while after it is stopped ·····0-4
●Be careful when opening/closing the
radiator cap·········································0-4
●Replenish coolant only when
the coolant in the system is cold ··············0-4 ●Do not remove heat insulating material ·····0-4
|
Warning |
Exhaust gas is |
|
poisonous ···························0-4 |
|
|
●Ensure good ventilation while the |
|
|
engine is running··································0-4 |
|
|
Warning |
Hearing difficulty ·················0-4 |
|
●Wear ear protector································0-4 |
|
|
Warning |
Beware of falling engine ·····0-5 |
●Exercise caution when lifting the engine ····0-5
●Do not climb on the engine ·····················0-5
●Secure your foothold when carrying out service···············································0-5
|
Caution |
Use correct engine oil |
|
and LLC······························0-5 |
●Only use the specified fuel, engine oil
and coolant (LLC)·································0-5
●Handle LLC with care ····························0-5
●Lawful disposal of waste oil and
coolant···············································0-5
|
Caution |
Handling of battery··············0-6 |
|
●Handle the battery with care····················0-6 |
|
|
Caution |
How to handle |
|
emergencies ·······················0-6 |
●Engine overheat — Idle to cool down,
then stop the engine ·····························0-6
●Never restart the engine after a sudden
stop unless the cause is eliminated ··········0-6
●Stop the engine immediately upon oil
pressure drop ······································0-6
●Stop the engine immediately upon broken
fan belt···············································0-6
|
Caution |
How to handle |
|
emergencies ·······················0-6 |
●Engine overheat — Idle to cool down,
then stop the engine ·····························0-6
●Never restart the engine after a sudden
stop unless the cause is eliminated ··········0-6
●Stop the engine immediately upon oil
pressure drop ······································0-6
●Stop the engine immediately upon broken
fan belt···············································0-6
Caution Other considerations···········0-7
●Never alter or modify the engine ··············0-7
●Do not tamper with sealing ·····················0-7
●Daily and periodical inspection ················0-7
●Running-in period ·································0-7
●Warming up the engine ··························0-7
●Do not overload the engine ·····················0-7 ●Cooling down the engine························0-7
●Do not spill water onto the engine ··········· 0-7 ●Air cleaner maintenance precautions ········0-8 ●Observe safety rules at work sites ············0-8
●Wear appropriate clothes and protective gear···················································0-8
●Use appropriate tools when carrying out service
0-8
●Do not operate the starter continuously
●The battery switch must be kept ON while
the engine is running·····························0-8
●Precautions for road transport ·················0-8

SAFETY CAUTIONS

●Never use open fire
When topping up or replacing fuel or engine oil, or cleaning parts in
wash oil, do not light a match, smoke or use any other open fire nearby. Doing these is extremely
dangerous as fuel and oils can catch fire. Completely wipe off any spilt fuel or engine oil as they are flammable and can be a fire hazard.
Store fuel and engine oil in a well-ventilated place. Firmly tighten the cap of the container.
●Pay attention to fuel and oil leakage
If leakage of fuel or oil is found, immediately take measures to stop it.
If leaking fuel or engine oil spills over the heated engine, fire may start, possibly leading to bodily injury or equipment damage.
●Use explosion-proof light
When checking fuel, engine oil, coolant, battery electrolyte, etc., use explosion-proof light. If ordinary light is used, these fluids may ignite and explode.
●Keep things tidy around the engine
Keep fuel, engine oil or any other flammables as well as explosives and other dangerous materials away from the engine. These materials can ignite and explode.
Keep the engine and the surrounding area free of waste, dirt, foreign matter, etc. These substances can be a fire hazard and invite overheating. In particular, ensure that the top of the battery is clean after service operations. Any waste left on the battery can cause short circuit.
Keep a running engine at least 1 m (3.3 ft.) away from the surrounding building or equipment to eliminate the risk of fire.
●Do not open the crankcase until it has cooled down
Do not attempt to open the crankcase side cover immediately after the engine is stopped. Wait at least 10 minutes until the engine has sufficiently cooled down.
If fresh air flows into the crankcase with the engine still hot, the remaining mist of oil may ignite and cause explosion.
●Prevent short circuit
Before inspecting or servicing the electrical/electronic system, disconnect the negative (-) cable from the battery terminal. Failure to observe this can cause the circuit to short, possibly starting a fire.
Loose terminals and damaged cables/wires can cause short circuit or even fire. Before carrying out service operation, check for loose or damaged components and repair or replace as required.
●Keep fire extinguisher and first-aid kit at hand
Keep a fire extinguisher at hand. Become familiar with the handling of the fire extinguisher.
Store a first-aid kit at the designated place. The kit should be kept fully
supplied so that it can serve the purpose at any time. Establish a set of actions to take in the event of fire or accident, including emergency contact numbers and means of communication.
0 — 2
SAFETY CAUTIONS

●Keep guards on the rotating parts
Ensure that all guards are correctly installed over the rotating parts of
the engine. Damaged or loose guards should be repaired. Never attempt to remove the
camshaft cover, rocker cover or any other guards form rotating parts while the engine is running. Never leave exposed the drive belts and related couplers for auxiliaries and radiator. They should also be covered with guards.
Never remove these guards.
●Ensure safety in the surrounding area when starting the engine
Before starting the engine, ensure that no one is near the electric power generator and that no tools or foreign matter are left behind. Shout to people around you so that they will know you are starting the engine.
Never start the engine if a “Do not start” tag or any other similar message is posted on the starter switch, etc.
●Lockout/tagout
Perform lockout/tagout before carrying out any inspection/service.
Lockout/tagout is an ideal way of disconnecting the machine/equipment from the power source.
To lockout/tagout, remove the starter switch key, place the battery switch in the “OFF” position, and post a “Do not start” tag or other similar message on the starter switch.
The starter switch key should then be carried by the person who is going to perform inspection/service. If an air start system is used, close the air tank source valve and post a “Do not open” tag or other similar message.
●Always stop the engine before any inspection/service
Always stop the engine before performing any inspection/service. Never attempt to adjust belt tension while the engine is running. Otherwise, the operator runs a great risk of becoming entangled into the rotating parts and seriously injured.
●Keep away from rotating parts while the engine is running
Never stand near the rotating parts
while the engine is running. Do not place objects near the rotating parts that are likely to be caught by
these parts.
Should any part of human body (or tool) is caught by the rotating parts, dismemberment or other bodily injury will result.
●Remove the turning gear after use
Be sure to remove the turning gear after use. Never start the engine with the turning gear still installed or “engaged.” Otherwise, the engine will break and possibly someone may become injured.
0 — 3

SAFETY CAUTIONS

●Do not touch the engine while it is running or for a while after it is
stopped
Never touch any part of the engine while it is running or for a while after
it is stopped. Otherwise, you may become burned.
Use a coolant temperature gauge to confirm that the engine has sufficiently cooled down before performing any inspection/service.
●Be careful when opening/closing the radiator cap
Never attempt to open the radiator cap while the engine is running and for a while after it is stopped. Stop the engine and wait until the coolant temperature has sufficiently dropped before opening the cap.
Slowly open the radiator cap to allow the internal pressure to escape. To prevent possible burn, wear thick rubber gloves or cover the cap with cloth to protect your hands from escaping vapor.
Tighten the radiator cap firmly.
Coolant is extremely hot while the engine is running or for a while after the engine is stopped. You may become burned by extremely hot vapor or coolant that will gush out if the radiator cap is opened.
●Replenish coolant only when the coolant in the system is cold
Do not replenish coolant for a while after the engine is stopped. Replenish coolant when the coolant in the system is sufficiently cold. Otherwise, you may become burned.
●Do not remove heat insulating material
The exhaust system components become extremely hot and therefore are covered with heat insulating material. Never remove the material. If the material needs to be removed at all for inspection/service, be sure to install it again after the operation.

●Ensure good ventilation while the engine is running
If the engine is installed inside a building and the exhaust gas is directed outside through a duct, regularly check the duct for any leakage through the joints etc.
Do not run the engine in a building (warehouse, tunnel, etc.), confined space, or other poorly ventilated places if the engine is used for a portable generator. If the engine needs to be run in a building at all, ensure to direct the exhaust gas outside and provide sufficient ventilation. Also, take care not to direct the exhaust gas towards nearby plants or animals, if any.
Engine exhaust gas contains carbon monoxide and other substances that are harmful to humans. Running the engine in a poorly ventilated place can cause exhaust gas poisoning.

difficulty
●Wear ear protector
Wear ear protector whenever entering the engine room. Otherwise, the combustion and mechanical noises may cause you to develop hearing difficulty.
0 — 4
SAFETY CAUTIONS

falling engine
●Exercise caution when lifting the engine
The wire rope used to lift the engine should have enough strength to withstand the weight of the engine.
Attach the specified lifting gear onto the lifting hangers on the engine.
Ensure that the engine is well balanced when it is lifted by taking into account the engine’s center of gravity.
The angle of wire rope relative to the lifting hangers should be maintained at 60º or less. Above this, the hangers may be subjected to overload and break.
If direct contact between the wire rope and the engine is anticipated, protect them from damage by covering them with cloth or other soft material.
●Do not climb on the engine
Do not climb onto the engine, nor place a foot on the components on the side of the engine.
Otherwise, you may not only break the engine components but also fall and become injured.
Use a stool or a platform to work on the top of the engine. Be careful not to slip and fall.
●Secure your foothold when carrying out service
Use a stable stool or platform when working on the top of the engine or
other areas of the engine difficult to reach.
Do not use a rickety stool nor
substitute a box of parts. Otherwise, you may fall and become injured.
Do not leave anything on the stool.

●Only use the specified fuel, engine oil and coolant (LLC)
Only use the fuel, engine oil and coolant (LLC) that are specified in this manual. Handle them with sufficient care.
Using fluids other than those specified in this manual or incorrect use of those specified in this manual will lead to many problems and may possibly cause failures.
Use the specified engine oil and LLC according to the instructions of MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheets) issued by and available from the manufacturers.
●Handle LLC with care
LLC is a strong alkali. Be careful not to drink it by mistake or allow it to contact your eyes.
Old coolant (containing LLC) that has been drained off is toxic. Do not dispose of it carelessly. Dispose of it in accordance with the applicable laws and regulations.
●Lawful disposal of waste oil and coolant
Do not dispose of waste oil or coolant carelessly. Doing so is harmful to the environment and is prohibited by law.
Harmful substances such as waste oil and coolant should be disposed of in a manner that complies with the applicable laws and regulations.
0 — 5
SAFETY CAUTIONS

battery
●Handle the battery with care
Batteries emit hydrogen and oxygen gases, both of which are
flammable. Never use open fire or 

dropped below the minimum line. Otherwise, the battery may explode.
Be careful not to inadvertently place a metal object such as tool between the battery terminals.
Always disconnect the negative (-) terminal first, then the positive (+) terminal, from the battery. Always connect the positive (+) terminal first, then the negative (-) terminal, to the battery.
Recharge the battery in a well ventilated place, with all battery plugs removed.
The battery terminals should have a positive connection. Loose terminals can generate sparks, possibly causing the battery to explode.
Before servicing or performing electric welding on the electrical/electronic system, position the battery switch in the “OPEN/OFF” position or disconnect the negative (-) terminal of the battery to isolate the electrical/electronic circuit.
The battery electrolyte contains dilute sulfuric acid. Incorrect handling may lead to loss of eyesight or burn. Never drink battery electrolyte.
Wear protective goggles and rubber gloves when maintaining the battery (replenishing, recharging, etc.).
If your skin or clothing has come into contact with battery electrolyte, immediately wash the affected area with plenty of water and then thoroughly clean with soap.
Should your eyes come into contact with battery electrolyte, loss of eyesight may result. Immediately wash your eyes with plenty of fresh water and seek medical attention immediately.
Should you inadvertently drink battery electrolyte, repeatedly gargle with plenty of water and then drink plenty of water. Seek medical attention immediately.

●Engine overheat — Idle to cool down, then stop the engine
In the event of engine overheat, do not stop the engine immediately. Doing so may cause the coolant temperature to rise quickly and the engine may seize. Instead, run the engine at low idle for a while to cool it down. Then, stop the engine. Do not attempt to replenish coolant for a while after the engine is stopped. Otherwise, the cylinder head etc., which may still be hot, is cooled down rapidly and may break. Wait until the engine is sufficiently cold and then top up slowly.
●Never restart the engine after a sudden stop unless the cause is eliminated
If the engine has suddenly stopped with some alert signals, do not restart immediately. Otherwise, the engine may seriously become damaged. Locate and eliminate the cause before restarting.
●Stop the engine immediately upon oil pressure drop
If the oil pressure has dropped, immediately stop the engine. Otherwise, bearings etc. may seize. Inspect the oil system and components.
●Stop the engine immediately upon broken fan belt
If the fan belt has broken, immediately stop the engine. Otherwise, the engine will overheat. Also, coolant vapor will gush out from the reserve tank and radiator and you may get burned.
0 — 6

SAFETY CAUTIONS

●Never alter or modify the engine
Altering or modifying the engine in any way will nullify the warranty.
A modified engine may not only break but also lead to injury.
●Do not tamper with sealing
To help ensure trouble-free operation of the engine, the fuel control link has been sealed to achieve the correct fuel injection volume and engine speed. If the sealed setting is tampered with, the following will result and the correct functioning of the engine is no longer guaranteed.
Sliding and rotating parts will wear faster.Various parts will seize/become damaged.The engine will consume more fuel and oil.The governor and fuel injection volume go out of
balance, reducing the engine performance.
●Warming up the engine
Before starting work, warm up the engine by running it at low idle for 5 to 10 minutes.
Warming up the engine will not only smoothen the operation of various engine parts but also help extend its service life. It also helps maximize the performance and achieve economical running of the engine.
Do not warm up the engine longer than necessary. Doing so facilitates carbon deposit on the cylinders, possibly leading to poor combustion.
●Do not overload the engine
Do not continue to run the engine if it emits black smoke.
Overloaded running of the engine (accompanied by black smoke) not only consumes excessive fuel but also facilitates carbon deposit and thus shortens the service life of the engine.
●Daily and periodical inspection
Perform the daily and periodical inspection in accordance with the Operation and Maintenance Manual.
Failure to observe the instructions of the manual may lead to many problems, and the various engine parts may eventually fail, possibly causing a serious accident.
●Running-in period
A brand new engine requires a running-in period of 50 hours, during which never put the engine under severe load. Otherwise, the service life of the engine will be reduced.
●Cooling down the engine
Before stopping the engine, cool it down (by running it at low idle) for 5 to 6 minutes.
Stopping the engine suddenly while it is heavily loaded will result in some areas of the engine remaining extremely hot for a while, which is detrimental to the long service life of an engine.
While the engine is being run at low idle for cooling, check the engine for any problems.
●Do not spill water onto the engine
Ensure that no rainwater etc. enters into the engine from the exhaust or inlet manifold, or via any other routes.
Do not run the engine while at the same time washing it. Otherwise, cleaning fluid (water) may be sucked into the engine.
If the engine is started with water trapped in the combustion chambers, water hammering will result, causing the engine to fail and possibly leading to a serious accident.
0 — 7

SAFETY CAUTIONS
●Air cleaner maintenance precautions
Wear of engine parts is accelerated largely by the dust contained in the intake air. Worn engine parts will lead to various problems such as increased oil consumption, reduced power and poor starting. Air cleaner is effective in removing dust in the intake air. When maintaining the air cleaner, observe the following precautions.
Never attempt to service the air cleaner while the engine is running.
When removing the air cleaner, take care not to allow the dust trapped on the air cleaner to enter into the inlet port.
If the engine is equipped with the dust indicator, clean the air filter only when the indicator shows clogging. Unnecessary maintenance (removal/ installation of the filter element) runs the risk of allowing dust into the inlet port or damaging/ deforming the filter element.
●Observe safety rules at work sites
Whenever running or servicing the engine, always observe the relevant safety rules in place.
If you are not in good shape, do not operate the engine. Consult the site supervisor.
Poor physical conditions are accompanied by reduced attention. Do not operate the engine if you are not feeling well. Otherwise, you may incorrectly handle the engine and cause an accident.
When working jointly with other people on the same task, use signals to coordinate actions involved.
●Wear appropriate clothes and protective gear
Whenever appropriate, including when using compressed air, wear protective gear such as helmet, face mask, safety shoes, dust mask, goggles and gloves.
Working without appropriate protective gear may lead to serious injury.
●Use appropriate tools when carrying out service
When carrying out any service, use appropriate tools and in correct ways.
Damaged tools should be replaced with new ones.
●Do not operate the starter continuously
Do not operate the starter more than 10 seconds per starting attempt. If the engine fails to start at the first attempt, wait for at least 30 seconds before trying again.
Do not run the starter continuously if the engine will not start. Otherwise, the battery will go flat or the starter will seize.
●The battery switch must be kept ON while the engine is running
Do not turn off the battery switch while the engine is running.
Otherwise, the instruments will become inoperative and the diode or transistor of the alternator may deteriorate.
●Precautions for road transport
When transporting the engine on public roads, the weight, width and height of the electric power generator should be taken into account while observing the relevant laws regarding road traffic and haulage, and vehicle restrictions and requirements.
0 — 8

GENERAL
1.Overview ····························································································· 1 — 2
1.1Outline Drawing ··················································································· 1 — 2
1.2Fuel System Schematic ········································································ 1 — 4
1.3Oil System Schematic··········································································· 1 — 4
1.4Cooling System Schematic ···································································· 1 — 5
1.5Inlet / Exhaust System Schematic ··························································· 1 — 5
1.6Engine Serial Number··········································································· 1 — 6
1.7Engine Model and Application Codes ······················································ 1 — 6
2.Specifications ······················································································ 1 — 7
3.Disassembly / Reassembly Notes······················································· 1 — 9
3.1Disassembly ······················································································· 1 — 9
3.2Reassembly························································································ 1 — 9
GENERAL
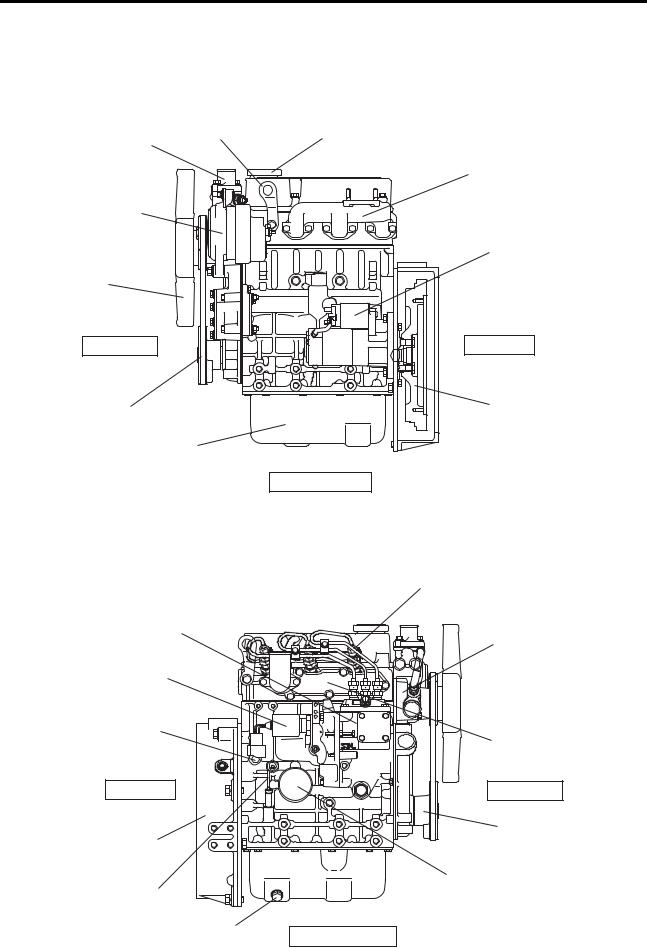
1. Overview
1.1 Outline Drawing
S3L, S3L2
|
Hanger |
Oil filler |
|
Thermostat |
Exhaust manifold
Alternator
Starter
Fan
|
Front end |
Rear end |
|
V belt |
Flywheel |
|
Oil pan |
|
|
Left-hand side |
|
|
Engine LH side view |
|
|
Fuel injection nozzle |
|
|
Fuel injection pump |
Water pump |
|
Stop solenoid |
|
|
Coolant drain plug |
|
|
Inlet cover |
|
|
Rear end |
Front end |
|
Flywheel housing |
Crankshaft pulley |
|
Oil filter |
|
|
Oil level gauge |
Oil drain plug
Right-hand side
Engine RH side view
1 — 2
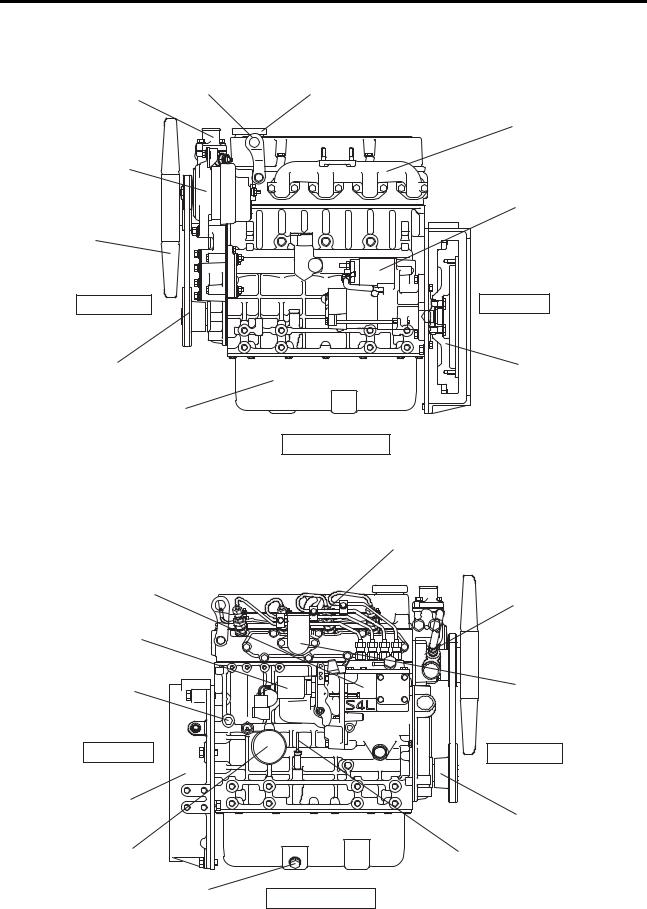
GENERAL
S4L, S4L2
Hanger
Thermostat
Alternator
Fan
Front end
V belt
Oil pan
Fuel injection pump
Stop solenoid
Coolant drain plug
Rear end
Flywheel housing
Oil filter
Oil drain plug
Oil filler
Exhaust manifold
Starter
Rear end
Flywheel
Left-hand side
Engine LH side view
Fuel injection nozzle
Water pump
Inlet cover
Front end
Crankshaft pulley
Oil level gauge
Right-hand side
Engine RH side view
1 — 3
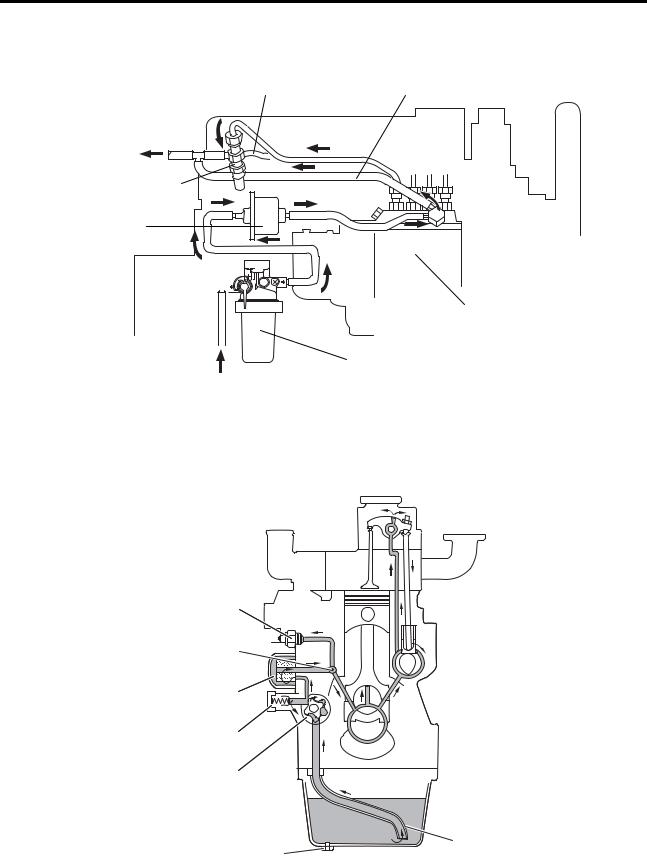
GENERAL
1.2 Fuel System Schematic
|
Fuel leak-off pipe |
Fuel injection pipe |
To fuel tank
Fuel injection nozzle
Fuel pump
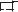
PE

Fuel injection pump
|
From fuel tank |
Fuel filter |
Fuel system schematic
1.3 Oil System Schematic
Oil pressure switch
Oil main gallery
Oil filter
Relief valve
Oil pump
Oil strainer
Oil drain plug
Oil system schematic
1 — 4
GENERAL
1.4 Cooling System Schematic
|
Water pump |
Water bypass valve |
|
Thermostat |
Radiator
Cooling fan
Cooling system schematic
1.5 Inlet / Exhaust System Schematic
Exhaust gas
Intake air
Air breather pipe
(positive crankcase Blow-by gas ventilation)
Intake air (from air cleaner)
Exhaust gas (to muffler)
Inlet cover
Exhaust manifold
Inlet / exhaust system schematic
1 — 5
GENERAL
1.6Engine Serial Number
The engine serial number is stamped on the top face of the fuel injection pump bracket on the right-hand side of the cylinder block.
Engine serial number location
1.7 Engine Model and Application Codes
(1)The engine model code is embossed on the side of the fuel injection pump mount on the
right-hand side of the cylinder block.
(2) The engine model code consists of the following alphanumerical digits.
Model coding
(Example) S 4 L 2
Engine model code
Type
(2 = Type 2)
Series
[L = bore size 78 mm (3.07 in.)]
No. of cylinders (4 = 4 cylinders)
S = Sagamihara Machinery Works
1 — 6
|
GENERAL |
||||||||||||
|
2. |
Specifications |
|||||||||||
|
Engine Type |
S3L |
S3L2 |
S4L |
S4L2 |
||||||||
|
Type |
Water- |
cooled; 4-stroke |
cycle; Diesel |
powered |
||||||||
|
No. of cylinders |
3 |
4 |
||||||||||
|
Combustion |
Swirl chamber type |
|||||||||||
|
Valve mechanism |
Overhead valve type |
|||||||||||
|
Cylinder bore×stroke |
mm (in.) |
78×78.5 |
78×92 |
78×78.5 |
78×92 |
|||||||
|
(3.07×3.09) |
(3.07×3.62) |
(3.07×3.09) |
(3.07×3.62) |
|||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>General |
Total displacement |
l (U.S. gal) |
1.125 |
1.318 |
1.500 |
1.758 |
||||||
|
(0.297) |
(0.348) |
(0.396) |
(0.464) |
|||||||||
|
Compression ratio |
22.0 |
: 1 |
||||||||||
|
Fuel |
Diesel fuel (JIS K2204 Special 1 — 3) |
|||||||||||
|
Firing order |
1-3-2 |
1-3-4-2 |
||||||||||
|
Direction of rotation |
Counterclockwise when viewed from the flywheel end |
|||||||||||
|
Dimensions |
Overall length |
mm (in.) |
536 (21.10) |
620 (24.40) |
||||||||
|
Overall width |
mm (in.) |
433 (17.04) |
433 (17.04) |
|||||||||
|
Overall height |
mm (in.) |
572 (22.52) |
572 (22.52) |
|||||||||
|
Dry mass |
kg (lb) |
135 (297.6) |
155 (341.7) |
|||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>parts |
Piston ring |
No. of rings |
Compression |
ring :2 |
||||||||
|
Oil ring (w/expander) : 1 |
||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>main |
Valve |
Inlet valve |
Open |
BTDC 15° |
||||||||
|
Close |
ABDC 41° |
|||||||||||
|
timing |
||||||||||||
|
Open |
BBDC 54° |
|||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Engine |
(hot engine) |
Exhaust valve |
||||||||||
|
Close |
ATDC 10° |
|||||||||||
|
Engine mounting |
4 mounts |
|||||||||||
|
Starting method |
Starter |
|||||||||||
|
Type |
Bosch M |
|||||||||||
|
Manufacturer |
DENSO |
|||||||||||
|
Injection |
Plunger |
mm (in.) |
φ5.5 (0.21) |
|||||||||
|
diameter |
||||||||||||
|
pump |
||||||||||||
|
MS retard |
8° |
|||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>system |
(crank angle) |
|||||||||||
|
Cam lift |
mm(in.) |
15 (0.59) |
||||||||||
|
Governor |
Governing method |
Centrifugal fly-weight type |
||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Fuel |
Type |
Throttle nozzle |
||||||||||
|
Injection |
Manufacturer |
Bosch Automotive Systems Corporation |
||||||||||
|
Spray angle |
mm (in.) |
15° |
||||||||||
|
nozzle |
Opening |
MPa |
14.22 to 15.00 (145 to 153) |
|||||||||
|
(kgf/cm2) |
||||||||||||
|
pressure |
[psi] |
[2062 to 2176] |
||||||||||
|
Fuel filter |
Type |
Paper-element cartridge; Separate type w/ cock |
||||||||||
|
Lubrication |
method |
Forced circulation (pressure feed by trochoid pump) |
||||||||||
|
Engine oil |
Grade |
CD Class (API Classification) |
||||||||||
|
Capacity |
l (U.S. gal) |
3.7 (1.0) |
4.2 (1.1) |
5.4 (1.4) |
6.0 (1.6) |
|||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>system |
(entire engine) |
|||||||||||
|
Oil pump |
Type |
Gear |
pump |
|||||||||
|
Displacement |
l (U.S. gal) |
18 (4.8) |
||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Oil |
/min |
|||||||||||
|
Type |
Piston valve |
|||||||||||
|
Relief valve |
Opening |
MPa |
0.35±0.05 (3.6±0.5) |
|||||||||
|
(kgf/cm2) |
||||||||||||
|
pressure |
[psi] |
[51±7] |
||||||||||
|
Oil filter |
Type |
Paper element (spin-on type) |
1 — 7

GENERAL
|
Engine Type |
S3L |
S3L2 |
S4L |
S4L2 |
|||||||||
|
Cooling method |
Water-cooled, |
forced circulation |
|||||||||||
|
Capacity (engine proper) |
l (U.S. gal) |
1.8 (0.5) |
2.5 (0.7) |
||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>system |
Water pump |
Type |
Centrifugal |
pump |
|||||||||
|
Displacement |
l (U.S. gal) |
30 (8.0) up (@ 2000 min-1 engine speed) |
|||||||||||
|
/min |
|||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Cooling |
Thermostat |
Type |
Wax |
||||||||||
|
Opening |
(°) |
82±1.5 (179.6±2.7) |
|||||||||||
|
temperature |
|||||||||||||
|
Cooling fan |
Type |
Pusher suction (PP fan) |
|||||||||||
|
No. of blades / OD |
5 / 340 (13.39), 6 / 320 (12.6), 6 / 340 (13.39), |
||||||||||||
|
mm (in.) |
6 / 360 (14.17), 6 / 380 (14.96), 7 / 380 (14.96) |
||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>system |
|||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>entl |
Air cleaner |
Type |
Paper element |
||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>I |
|||||||||||||
|
Voltage — Polarity |
12 V — Θ ground, 24 V — Θ ground |
||||||||||||
|
Type |
M001T68281, M008T70471A, M008T81071A |
||||||||||||
|
Manufacturer |
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation |
||||||||||||
|
Pinion |
Pinion shift (reduction) |
||||||||||||
|
Starter |
engagement |
||||||||||||
|
Output |
V-kW |
12 V-1.7, 12 V-2.0, 24 V-3.2 |
|||||||||||
|
No. of units |
1 |
||||||||||||
|
Reduction ratio |
13 / 120 |
||||||||||||
|
(pinion / ring gear) |
|||||||||||||
|
Type |
3-phase alternator w/ built-in IC regulator |
||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>system |
Manufacturer |
Mitsubishi Electric Corporation |
|||||||||||
|
rated voltage is |
min-1 |
5000 (@ 13.5 V, 47 A), 5000 (@ 27.0 V, 22 A) |
|||||||||||
|
Alternator |
Output |
V-A |
12-50, 24-25 |
||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Electrical |
Speed at which |
||||||||||||
|
Type |
Sheathed plug |
||||||||||||
|
generated |
|||||||||||||
|
Regulated voltage |
V |
14.7±0.3 (12-50), 26.5±0.5 (24-25) |
|||||||||||
|
Glow plug |
Rated voltage — |
V-A |
12 V plug |
24 V plug |
|||||||||
|
10.5-9.7 |
22.5-5 |
||||||||||||
|
current |
|||||||||||||
|
(30-second application) |
(25-second application) |
||||||||||||
|
Operating |
V |
12 V-ETR |
12 V-ETS |
24 V-ETR |
24 V-ETS |
||||||||
|
voltage |
8 or less |
10 to 15 |
16 or less |
20 to 30 |
|||||||||
|
Insulation resistance |
100 MΩ or more at DC500 V |
||||||||||||
|
Stop |
(at ordinary temperature and humidity) |
||||||||||||
|
solenoid |
Stroke |
mm (in.) |
13.5±0.5 (0.53±0.01) |
||||||||||
|
Working |
-40 to 120 |
-30 to 120 |
-40 to 120 |
-30 to 120 |
|||||||||
|
ambient |
(°) |
||||||||||||
|
(-40 to 248) |
(-22 to 248) |
(-40 to 248) |
(-22 to 248) |
||||||||||
|
temperature |
1 — 8

GENERAL
3. Disassembly / Reassembly Notes
This Service Manual specifies various procedures recommended by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. for servicing Mitsubishi diesel engines. These procedures include, wherever appropriate, required special tools and related safety precautions.
The instructions provided in this manual, however, cannot fully guarantee safety as potential risks beyond ordinary imagination are hidden everywhere.
When conduct any work, the following points should also be observed in addition to the instructions this manual.
3.1 Disassembly
(1)Use tools and equipment that are appropriate for the work being carried out.
(2)Whenever necessary, use workbenches to work on or sort parts out. Disassemble in accordance with the disassembly sequence given in the manual.
(3)As parts are disassembled, place them neatly in the order of removal to eliminate missing parts on reassembly.
(4)During disassembly, note the assembly marks. Remember to respect these marks on reassembly. Whenever appropriate, put additional assembly marks to aid reassembly.
(5)Before and during disassembly as well as during subsequent washing, carefully check for any abnormality or other fault which otherwise may likely remain unnoticed afterwards.
(6)Pay sufficient attention to ensure safety, especially when lifting or carrying heavy components and parts. (Use a jack or a chain block as required.)
3.2 Reassembly
(1)Parts excluding oil seals, O-rings, rubber sheets, etc. should be thoroughly washed in wash oil and completely dried using compressed air.
(2)Use appropriate tools and equipment.
(3)Use good-quality oil and grease. Never fail to apply oil, grease, sealant and adhesive to the relevant locations if so instructed in the manual.
1 — 9

GENERAL
(4)Tighten hardware to the specified torque, if provided in the manual. Be sure to use a torque wrench.
(5)Gaskets, packing and O-rings should be replaced with new parts unless specified otherwise.
1 — 10

SERVICE STANDARDS
1.Service Standards Table····································································· 1 -12
2.Tightening Torques Table···································································· 1 -16
2.1Major Bolts and Nuts ··········································································· 1 -16
2.2Standard Bolts and Nuts······································································· 1 -17
2.3Standard Eyebolts ··············································································· 1 -17
2.4Standard Union Nuts ··········································································· 1 -18
2.5Taper Bolts ························································································ 1 -18
3.Sealants List······················································································· 1 -19

SERVICE STANDARDS
1. Service Standards Table
Unit: mm (in.)
<![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Group
<![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Engine general
<![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Engine main parts
|
Item |
Nominal |
Standard value |
Limit |
Remarks |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
value |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Max. speed |
+30 |
-1 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(based on the rated speed) |
2700-10 |
min |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Min. speed |
1000±25 min-1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Compression pressure |
2.9 MPa (30 kgf/cm2) |
2.6 MPa |
2 |
Both oil and coolant |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
[421 psi] |
(27 kgf/cm ) |
temperatures at 20 to |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(at 290 min-1) |
[377 psi] |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
or above |
or less |
30 (68 to 86°) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
0.29 to 0.39 MPa |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Engineoil |
<![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>pressure |
Rated speed |
(3.0 to 4.0 kgf/cm2) |
Oil temperature at |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Low idle speed |
(1.0 kgf/cm2) |
194°) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
[42.07 to 56.57 psi] |
60 to 95 (140 to |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
0.098 MPa |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
[14.22 psi] |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Inlet valve |
BTDC 15° |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Valve timing [with |
open |
The theoretical valve |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Inlet valve |
ABDC 41° |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2 mm (0.079 in.) |
closed |
timing figures for |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
clearance on the |
inspection vary from |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Exhaust valve |
BBDC 54° |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
valve side; cold |
the actual valve |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
open |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
engine] |
timing. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Exhaust valve |
ATDC 10° |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
closed |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Valve clearance |
Inlet valve |
0.25 (0.01) |
Cold engine |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Exhaust valve |
0.25 (0.01) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Fuel injection timing |
(BTDC) |
17° |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Rocker arm inner diameter |
φ19 |
18.910 to |
18.930 |
― |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(0.749) |
(0.7450 to |
0.7458) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Rocker |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Rocker shaft diameter |
φ19 |
18.880 to |
18.898 |
― |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(0.749) |
(0.7438 to |
0.7445) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Arm-to-shaft clearance |
0.012 to |
0.050 |
0.200 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(0.0004 |
Replace rocker arm. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(oil clearance) |
(0.0079) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
to 0.0019) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Inlet |
φ6.6 |
6.565 to |
6.580 |
6.500 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Valve stem diameter |
(0.260) |
(0.2586 to |
0.2592) |
(0.256) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Exhaust |
φ6.6 |
6.530 to |
6.550 |
6.500 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(0.260) |
(0.2572 to |
0.2580) |
(0.256) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Valve |
Inlet |
φ6.6 |
6.600 to |
6.615 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Valve guide inner |
(0.260) |
(0.2600 to |
0.2606) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
diameter |
Exhaust |
φ6.6 |
6.600 to |
6.615 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(0.260) |
(0.2600 to |
0.2606) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Inlet |
0.020 to |
0.050 |
0.100 |
Replace valve and |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Valve stem-to-guide |
(0.0008 to |
0.0020) |
(0.004) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
clearance |
Exhaust |
0.050 to |
0.085 |
0.150 |
valve guide. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(0.0020 to |
0.0033) |
(0.006) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Valve seat angle |
45° |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>valve |
Valve seat |
width |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Valve head sinkage |
0 |
0.25 to |
0.75 |
1.5 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(0.0098 to |
0.0295) |
(0.0591) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>and |
Valve seat width |
1.6 |
1.30 to |
1.80 |
2.5 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(0.063) |
(0.0512 to |
0.0709) |
(0.0985) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>seat |
Valve |
Valve |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Valve head margin |
1.5 |
1.35 to |
1.65 |
0.5 |
seat |
Valve |
head |
head |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Valve |
(0.0591) |
(0.0531 to |
0.0650) |
(0.0197) |
angle |
sinkage |
margin |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Installed valve guide protrusion |
10 |
9.5 to 10.5 |
― |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(0.394) |
(0.3743 to |
0.4137) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1 — 12

SERVICE STANDARDS
<![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Group
<![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Engine main parts
|
Unit: mm (in.) |
||||||||||||||||
|
Item |
Nominal |
Standard value |
Limit |
Remarks |
||||||||||||
|
value |
||||||||||||||||
|
Free length |
47 (1.85) |
46 (1.81) |
||||||||||||||
|
θ |
θ=2.0° |
= 0.5 |
||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>spring |
=0.2 |
|||||||||||||||
|
Squareness |
(0.0197) |
|||||||||||||||
|
(0.0079) |
||||||||||||||||
|
across the |
||||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Valve |
Lf=47 |
entire length |
||||||||||||||
|
(1.8518) |
||||||||||||||||
|
Installed length / load |
39.0 (1.536)/ |
30.1 (1.185)/ |
||||||||||||||
|
131 to 145 |
279 to 309 |
-15 % |
||||||||||||||
|
mm (in.)/N (kgf) [lbf] |
(13.3 to 14.7) |
(28.5 to 31.5) |
||||||||||||||
|
[29 to 33] |
[63 to 69] |
|||||||||||||||
|
Push rod |
Bend |
― |
0.3 (0.011) |
Replace |
||||||||||||
|
Cylinder head |
Bottom face |
0.05 (0.002) |
0.10 (0.004) |
Correct |
||||||||||||
|
distortion |
or less |
|||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Cylinder |
||||||||||||||||
|
Cylinder block top face |
φ78 |
0.05 (0.002) |
0.10 (0.004) |
Correct |
||||||||||||
|
+0.03 |
+0.0012 |
|||||||||||||||
|
distortion |
or less |
|||||||||||||||
|
Bore |
(3.07) |
78.0 0 |
(3.07 0 |
) |
78.2 (3.08) |
Bore or replace |
||||||||||
|
Out of roundness |
±0.01 (0.0004) |
― |
||||||||||||||
|
or less |
||||||||||||||||
|
STD |
78.00 |
77.93 to |
77.95 |
77.80 |
||||||||||||
|
(3.07) |
(3.070 to 3.071) |
(3.065) |
||||||||||||||
|
Diameter |
0.25 OS |
78.25 |
78.18 to |
78.20 |
78.05 |
|||||||||||
|
(3.08) |
(3.080 to 3.081) |
(3.075) |
||||||||||||||
|
0.50 OS |
78.50 |
78.43 to |
78.45 |
78.30 |
||||||||||||
|
(3.09) |
(3.090 to 3.090) |
(3.085) |
||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Piston |
Max. allowable |
variation in |
or less |
|||||||||||||
|
weight among pistons on the |
±5 g (0.177 oz) |
― |
||||||||||||||
|
same engine |
||||||||||||||||
|
Piston pin diameter |
φ23 |
22.944 to |
23.000 |
― |
||||||||||||
|
(0.9062) |
(0.9039 to |
0.9062) |
||||||||||||||
|
Piston pin-to-boss clearance |
0.006 to |
0.018 |
0.050 |
|||||||||||||
|
(0.0002 to |
0.0007) |
(0.002) |
||||||||||||||
|
Piston-to-cylinder clearance |
0.035 to |
0.086 |
0.300 |
Bore or replace |
||||||||||||
|
(0.0014 to |
0.0034) |
(0.012) |
||||||||||||||
|
No. 1 ring |
0.09 to 0.11 |
0.300 |
||||||||||||||
|
Piston |
(0.0035 to |
0.0043) |
(0.012) |
|||||||||||||
|
0.07 to 0.11 |
0.200 |
|||||||||||||||
|
ring-to-groove |
No. 2 ring |
Replace piston ring |
||||||||||||||
|
(0.0028 to |
0.0043) |
(0.008) |
||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>ring |
clearance |
|||||||||||||||
|
Oil ring |
0.03 to |
0.07 |
0.200 |
|||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Piston |
(0.0012 to |
0.0028) |
(0.008) |
|||||||||||||
|
No. 1 ring |
(0.006 to 0.012) |
|||||||||||||||
|
0.15 to |
0.30 |
|||||||||||||||
|
1.50 |
||||||||||||||||
|
Piston ring gap |
No. 2 ring |
0.15 to |
0.35 |
Replace |
||||||||||||
|
(0.006 to 0.014) |
(0.06) |
|||||||||||||||
|
Oil ring |
0.20 to |
0.40 |
||||||||||||||
|
(0.008 to 0.016) |
||||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Connecting |
<![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>rod |
Bend and twist |
0.05/100 |
0.15/100 |
||||||||||||
|
(0.002/3.940) |
(0.006/3.940) |
|||||||||||||||
|
End play |
0.10 to |
0.35 |
0.50 |
Replace connecting |
||||||||||||
|
(0.004 to 0.014) |
(0.020) |
rod |
||||||||||||||
1 — 13

SERVICE STANDARDS
|
Unit: mm (in.) |
|||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Group |
Item |
Nominal |
Standard value |
Limit |
Remarks |
||||||
|
value |
|||||||||||
|
Crank journal diameter (STD) |
φ52 |
51.985 to |
52.000 |
― |
|||||||
|
(2.0488) |
(2.0482 to |
2.0488) |
|||||||||
|
Crank pin diameter |
φ48 |
47.950 to |
47.964 |
― |
|||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Crankshaft |
(1.8912) |
(1.8892 to |
1.8897) |
||||||||
|
Crankshaft bend |
0.025 (0.0010) |
0.050 (0.0020) |
Correct or replace |
||||||||
|
Main bearings oil clearance |
0.030 to |
0.077 |
0.100 |
Replace main |
|||||||
|
(0.0012 to |
0.0030) |
(0.0040) |
bearings |
||||||||
|
Connecting rod bearings oil |
0.025 to |
0.072 |
0.150 |
Replace connecting |
|||||||
|
clearance |
(0.0010 to |
0.0028) |
(0.0059) |
rod bearings |
|||||||
|
End play |
0.050 to |
0.175 |
0.500 |
Replace flanged No. |
|||||||
|
(0.0020 to |
0.0069) |
(0.0197) |
3 main bearings |
||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>backlashgear |
Crank gear to idler gear |
||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>partsmain |
Idler gear to valve camshaft |
0.040 to |
0.120 |
||||||||
|
gear |
|||||||||||
|
(0.0015 to |
0.0047) |
||||||||||
|
Idler gear to pump camshaft |
0.300 |
Replace |
|||||||||
|
gear |
|||||||||||
|
(0.0120) |
|||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Engine |
<![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Timing |
Valve camshaft gear to PTO |
0.080 to |
0.190 |
|||||||
|
gear |
(0.0032 to |
0.0075) |
|||||||||
|
Pump camshaft gear to oil |
0.070 to |
0.200 |
|||||||||
|
pump gear |
(0.0028 to |
0.0079) |
|||||||||
|
Camshaft cam height |
35.720±0.1 |
34.720 |
Replace |
||||||||
|
(including lobe) |
(1.4073±0.0394) |
(1.3679) |
|||||||||
|
Fuel injection pump shaft cam |
44±0.1 |
43 |
Replace |
||||||||
|
height (including lobe) |
(1.7336±0.0039) |
(1.6942) |
|||||||||
|
Flywheel flatness |
0.150 (0.0059) |
0.500 |
Correct |
||||||||
|
or less |
(0.0197) |
||||||||||
|
Tappet-to-guide clearance |
― |
0.150 |
Replace tappet |
||||||||
|
(0.0059) |
|||||||||||
|
Camshaft journal-to-bushing |
0.050 to |
0.125 |
0.150 |
Replace bushing |
|||||||
|
clearance |
(0.0020 to |
0.0049) |
(0.0059) |
||||||||
|
Idler gear-to-shaft clearance |
0.020 to |
0.070 |
0.200 |
Replace idler gear or |
|||||||
|
(0.0008 to |
0.0028) |
(0.0079) |
idler shaft |
||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>system |
Injection valve opening pressure |
(145) |
(145 to 153) |
― |
Adjust with washer |
||||||
|
14.22 |
14.22 to |
15.00 |
|||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Fuel |
MPa (kgf/cm2) [psi] |
[2062] |
[2062 to 2176] |
||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>system |
Relief valve opening pressure |
0.35±0.05 |
Replace |
||||||||
|
MPa (kgf/cm2) [psi] |
(3.5±0.5) |
― |
|||||||||
|
[50 |
± |
||||||||||
|
7.2] |
|||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Oil |
Oil pressure switch closing pressure |
0.05±0.01 |
Replace |
||||||||
|
MPa (kgf/cm2) [psi] |
(0.5±0.1) |
― |
|||||||||
|
± |
1.4] |
||||||||||
|
[7 |
|||||||||||
|
Valve opening |
82±1.5 |
― |
|||||||||
|
temperature |
(179.6±2.7°) |
||||||||||
|
Thermostat |
Replace |
||||||||||
|
8 mm (0.32 in.) |
95 |
||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>system |
valve lift |
― |
|||||||||
|
(203°) |
|||||||||||
|
temperature |
|||||||||||
|
At 111±3.5 |
30 MΩ |
||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Cooling |
Thermoswitch |
[when dipped in oil of |
― |
Replace |
|||||||
|
(231.8±6.3°) |
|||||||||||
|
105 (221°)] |
|||||||||||
|
Fan belt deflection |
{when pressed |
||||||||||
|
with a force of approx. 98 N (10 |
10 to |
12 |
Replace |
||||||||
|
kgf) [22] between crankshaft and |
― |
||||||||||
|
(0.4 to |
0.5) |
||||||||||
|
alternator pulleys and between |
|||||||||||
|
crankshaft and fan pulleys} |
1 — 14

SERVICE STANDARDS
Unit: mm (in.)
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Group |
Item |
Nominal |
Standard value |
Limit |
Remarks |
|||||||||||||
|
value |
||||||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>t |
||||||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>exhaus |
Paper-element type air |
Clean every 100 hours |
Replace every |
|||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>systems |
cleaner |
500 hours |
||||||||||||||||
|
Inlet / exhaust manifold |
0.15 (0.006) |
Grind or |
||||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>and |
― |
|||||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>let |
mounting face distortion |
or less |
replace |
|||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>In |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Pinion gap |
0.5 to 2.0 |
― |
Adjust with |
|||||||||||||||
|
(0.02 to 0.08) |
packing |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Terminal |
M001T68281 |
M008T70471A |
M008T81071A |
― |
||||||||||||||
|
No-load |
voltage |
11 V |
11 V |
23 V |
||||||||||||||
|
110 A |
130 A |
80 A |
Inspect |
|||||||||||||||
|
character- |
Current |
― |
||||||||||||||||
|
istics |
or less |
or less |
or less |
|||||||||||||||
|
Rotation |
2400 |
3600 |
3000 |
― |
||||||||||||||
|
speed |
min-1 |
min-1 |
min-1 |
|||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Starter |
16.5 |
18.0 |
M001T68281 |
M008T70471A, |
||||||||||||||
|
Brush length |
M008T81071A |
Replace |
||||||||||||||||
|
(0.65) |
(0.71) |
10.0 |
11.0 |
|||||||||||||||
|
(0.39) |
(0.43) |
|||||||||||||||||
|
17.5 to |
||||||||||||||||||
|
23.7 N |
29.4 to 39.2 N |
6.90 N |
13.7 N |
|||||||||||||||
|
(1.78 to |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Brush spring load |
(3.0 to 4.0 kgf) |
(0.70 kgf) |
(1.40 kgf) |
Replace |
||||||||||||||
|
2.41 kgf) |
||||||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>system |
[6.6 to 8.8 lbf] |
[1.6 lbf] |
[3.1 lbf] |
|||||||||||||||
|
[3.9 to 5.3 |
||||||||||||||||||
|
lbf] |
||||||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Electrical |
Commutator radial |
0.05 |
0.03 |
0.10 |
Correct or |
|||||||||||||
|
runout |
(0.002) |
(0.001) |
(0.004) |
replace |
||||||||||||||
|
Commutator diameter |
29.4 |
32.0 |
28.8 |
31.4 |
Replace |
|||||||||||||
|
(1.16) |
(1.26) |
(1.13) |
(1.24) |
|||||||||||||||
|
Mica undercutting |
0.5 |
0.2 |
Correct |
|||||||||||||||
|
depth |
(0.02) |
(0.01) |
||||||||||||||||
|
IC regulator |
A007T02071C |
A007TA8571 |
― |
|||||||||||||||
|
controlled voltage |
||||||||||||||||||
|
14.7±0.3 V |
28.5±0.5 V |
|||||||||||||||||
|
[at 20 (68°)] |
||||||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>istics |
2500 |
Terminal |
13.5 V |
27.0 V |
― |
|||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>Alternator |
min-1 |
voltage |
||||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>(when |
min-1 |
voltage |
||||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>h aracter c |
or |
Terminal |
||||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>hot) |
less |
Current |
32 A or above |
18 A or above |
― |
|||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>utput |
5000 |
13.5 V |
27.0 V |
― |
||||||||||||||
|
or |
||||||||||||||||||
| <![if ! IE]>
<![endif]>O |
Current |
47 A or above |
22 A or above |
― |
||||||||||||||
|
less |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Brush length |
18.5 |
(0.73) |
5.0 (0.20) |
Replace |
||||||||||||||
|
Clearance between stop |
0.15 to 0.20 |
Correct |
||||||||||||||||
|
solenoid plunger and rack |
(0.006 to 0.008) |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Glow plug resistance |
0.55 Ω |
― |
Replace |
1 — 15

SERVICE STANDARDS
2. Tightening Torques Table
2.1 Major Bolts and Nuts
|
Thread |
Tightening torque |
||||||||
|
Fittings |
diameter |
||||||||
|
Remarks |
|||||||||
|
×pitch |
N m |
kgf m |
lbf ft |
||||||
|
(mm) |
|||||||||
|
Engine proper |
|||||||||
|
Cylinder head bolt |
M10×1.75 |
83.4 to 93.2 |
8.5 to 9.5 |
61.5 to 68.7 |
|||||
|
Rocker cover bolt |
M8×1.25 |
9.81 to 12.7 |
1.0 to 1.3 |
7.2 to 9.4 |
|||||
|
Rocker shaft bracket bolt |
M8×1.25 |
9.81 to 19.6 |
1.0 to 2.0 |
7.2 to 14.5 |
|||||
|
Thrust plate bolt |
M8×1.25 |
9.8 to 11.8 |
1.0 to 1.2 |
7.2 to 8.7 |
|||||
|
Main bearing cap bolt |
M10×1.25 |
49.0 to 53.9 |
5.0 to 5.5 |
36.2 to 39.8 |
|||||
|
Connecting rod cap nut |
M9×1.0 |
32.4 to 37.3 |
3.3 to 3.8 |
23.9 to 27.5 |
|||||
|
Flywheel bolt |
M12×1.25 |
127 to 137 |
13.0 to 14.0 |
94.0 to 101.3 |
|||||
|
Crankshaft pulley nut |
M18×1.5 |
147 to 196 |
15.0 to 20.0 |
108.5 to 144.6 |
|||||
|
Rear plate mounting bolt |
M12×1.25 |
53.9 to 73.5 |
5.5 to 7.5 |
39.8 to 54.2 |
Equivalent to 7T |
||||
|
Fuel system |
|||||||||
|
Hollow screw |
M14×1.5 |
19.6 to 24.5 |
2.0 to 2.5 |
14.5 to 18.1 |
|||||
|
(fuel injection pump) |
|||||||||
|
Delivery valve holder |
― |
39.2 to 49.0 |
4.0 to 5.0 |
28.9 to 36.1 |
|||||
|
(fuel injection pump) |
|||||||||
|
Air bleeder plug |
M8×1.25 |
9.81 to 13.7 |
1.0 to 1.4 |
7.2 to 10.1 |
|||||
|
(fuel injection pump) |
|||||||||
|
Nozzle retaining nut |
IDI |
M16×0.75 |
34.3 to 39.2 |
3.5 to 4.0 |
25.3 to 28.9 |
||||
|
Nozzle holder |
IDI |
M20×1.5 |
49.0 to 58.8 |
5.0 to 6.0 |
36.2 to 43.4 |
||||
|
Fuel injection pipe nut |
M12×1.5 |
24.5 to 34.3 |
2.5 to 3.5 |
18.1 to 25.3 |
|||||
|
Fuel leak-off pipe nut |
M12×1.5 |
20.6 to 24.5 |
2.1 to 2.5 |
15.2 to 18.1 |
|||||
|
Sliding sleeve shaft |
M10×1.25 |
29.4 to 41.2 |
3.0 to 4.2 |
21.7 to 30.4 |
|||||
|
Torque spring set special nut |
M12×1.0 |
14.7 to 24.5 |
1.5 to 2.5 |
10.8 to 18.1 |
|||||
|
Oil system |
|||||||||
|
Oil relief valve |
M22×1.5 |
44.1 to 53.9 |
4.5 to 5.5 |
32.5 to 39.8 |
|||||
|
Oil pan drain plug |
M14×1.5 |
34.3 to 44.1 |
3.5 to 4.5 |
25.3 to 32.5 |
|||||
|
Oil filter |
M20×1.5 |
10.8 to 12.7 |
1.1 to 1.3 |
8.0 to 9.4 |
|||||
|
Oil pressure switch |
PT1/8 |
7.85 to 11.8 |
0.8 to 1.2 |
5.8 to 8.7 |
|||||
|
Oil pan mounting bolt |
M8×1.25 |
9.80 to 12.7 |
1.0 to 1.3 |
7.2 to 9.4 |
Equivalent to 4T |
||||
|
Oil strainer nut |
M16×1.5 |
24.5 to 29.4 |
2.5 to 3.0 |
18.1 to 21.7 |
|||||
|
Cooling system |
|||||||||
|
Thermoswitch |
M16×1.5 |
18.6 to 26.5 |
1.9 to 2.7 |
13.7 to 19.6 |
|||||
|
Thermostat cover bolt |
M8×1.25 |
16 to 20 |
1.6 to 2.0 |
11.8 to 14.8 |
|||||
|
Thermo case bolt |
M16×1.5 |
39.2 to 49.0 |
4.0 to 5.0 |
28.9 to 36.1 |
|||||
|
Inlet and exhaust systems |
|||||||||
|
Inlet cover bolt |
M8×1.25 |
14.7 to 21.6 |
1.5 to 2.2 |
10.8 to 15.9 |
|||||
|
Exhaust manifold bolt |
M8×1.25 |
14.7 to 21.6 |
1.5 to 2.2 |
10.8 to 15.9 |
|||||
|
Electrical system |
|||||||||
|
Starter terminal B |
M8×1.25 |
9.81 to 11.8 |
1.0 to 1.2 |
7.2 to 8.7 |
|||||
|
Stop solenoid fixing nut |
M30×1.5 |
39.2 to 49.0 |
4.0 to 5.0 |
28.9 to 36.1 |
|||||
|
Stop solenoid blind plug |
M30×1.5 |
39.2 to 49.0 |
4.0 to 5.0 |
28.9 to 36.1 |
|||||
|
Glow plug |
M10×1.25 |
14.7 to 19.6 |
1.5 to 2.0 |
10.8 to 14.5 |
1 — 16

SERVICE STANDARDS
2.2 Standard Bolts and Nuts
|
Thread |
4T |
7T |
|||||
|
diameter |
|||||||
|
N m |
kgf m |
lbf ft |
N m |
kgf m |
lbf ft |
||
|
×pitch (mm) |
|||||||
|
M6×1.0 |
2.94 to 4.90 |
0.3 to 0.5 |
2.2 to 3.6 |
7.85 to 9.80 |
0.8 to 1.0 |
5.8 to 7.2 |
|
|
M8×1.25 |
9.80 to 12.7 |
1.0 to 1.3 |
7.2 to 9.4 |
14.7 to 21.6 |
1.5 to 2.2 |
10.8 to 15.9 |
|
|
M10×1.25 |
17.7 to 24.5 |
1.8 to 2.5 |
0.7 to 1.0 |
29.4 to 41.2 |
3.0 to 4.2 |
21.7 to 30.4 |
|
|
M12×1.25 |
29.4 to 41.2 |
3.0 to 4.2 |
21.7 to 30.4 |
53.9 to 73.5 |
5.5 to 7.5 |
39.8 to 54.2 |
|
Note: (a) The above table shows the tightening torques for standard bolts and nuts.
(b)The values in the table apply when tightened together with spring washers.
(c)The above table shows standard values, for which a tolerance of ±10% is allowed.
(d)Unless otherwise specified, standard bolts and nuts should be tightened to the torques in the table.
(e)Do not apply oil to threaded portions (Tighten under dry conditions).
2.3Standard Eyebolts
|
Thread diameter |
Property class |
||
|
×pitch (mm) |
N m |
kgf m |
lbf ft |
|
M8×1.25 |
8±1 |
0.8±0.1 |
5.9±0.7 |
|
M10×1.25 |
15±2 |
1.5±0.2 |
11.1±1.5 |
|
M12×1.25 |
25±3 |
2.5±0.3 |
18.4±2.2 |
|
M14×1.5 |
34±4 |
3.5±0.4 |
25.1±3.0 |
|
M16×1.5 |
44±5 |
4.5±0.5 |
32.5±3.7 |
|
M18×1.5 |
74±5 |
7.5±0.5 |
54.6±3.7 |
|
M20×1.5 |
98±10 |
10.0±1.0 |
72.3±7.4 |
|
M24×1.5 |
147±15 |
15.0±1.5 |
108.4±10.8 |
|
M27×1.5 |
226±20 |
23.0±2.0 |
166.7±14.8 |
(Dry conditions)
1 — 17

SERVICE STANDARDS
|
2.4 Standard Union Nuts |
|||||
|
Nominal |
Cap nut size |
N m |
kgf m |
lbf ft |
|
|
diameter |
|||||
|
63 |
M14×1.5 |
39 |
4 |
28.8 |
|
|
80 |
M16×1.5 |
49 |
5 |
36.1 |
|
|
100 |
M20×1.5 |
78 |
8 |
57.5 |
|
|
120 |
M22×1.5 |
98 |
10 |
72.3 |
|
|
150 |
M27×1.5 |
157 |
16 |
115.8 |
|
|
180 |
M30×1.5 |
196 |
20 |
144.6 |
|
|
200 |
M30×1.5 |
196 |
20 |
144.6 |
|
|
220 |
M33×1.5 |
245 |
25 |
180.7 |
|
|
254 |
M36×1.5 |
294 |
30 |
216.8 |
|
|
(Dry conditions) |
2.5 Taper Bolts
|
Size |
Tightening into aluminum |
Tightening into iron |
|||||
|
N m |
kgf m |
lbf ft |
N m |
kgf m |
lbf ft |
||
|
NPTF1/16 |
4.90 to 7.85 |
0.5 to 0.8 |
3.6 to 5.8 |
7.85 to 11.8 |
0.8 to 1.2 |
5.8 to 8.7 |
|
|
PT1/8 |
7.85 to 11.8 |
0.8 to 1.2 |
5.8 to 8.7 |
14.7 to 21.6 |
1.5 to 2.2 |
10.8 to 15.9 |
|
|
PT1/4, NPTF1/4 |
19.6 to 29.4 |
2.0 to 3.0 |
14.5 to 21.7 |
34.3 to 44.1 |
3.5 to 4.5 |
25.3 to 32.5 |
|
|
PT3/8 |
― |
― |
― |
53.9 to 73.5 |
5.5 to 7.5 |
39.8 to 54.2 |
1 — 18
SERVICE STANDARDS
3. Sealants List
|
Sealing item |
Sealant |
Mating |
Applied location |
|
|
component |
||||
|
Stop solenoid |
ThreeBond 1212 |
Governor case |
||
|
Threaded part |
Water drain joint |
ThreeBond 1102 |
Block |
Threaded portion |
|
Oil pressure switch |
||||
|
Torque spring set |
ThreeBond 1212 |
Governor case |
||
|
Cylinder block |
||||
|
Sealing cap |
Cylinder head |
Holes in the cylinder |
||
|
Press — fit part |
ThreeBond 1102 |
Cylinder head, |
head and block |
|
|
Cylinder block |
||||
|
Expansion plug |
Cylinder block |
|||
|
Oil level gauge guide |
||||
|
Side seal |
Cylinder block, |
Outer periphery |
||
|
ThreeBond 1212 |
Main bearing cap |
|||
|
Main bearing cap |
Contact faces with the |
|||
|
Other |
||||
|
(front and rear) |
cylinder block |
|||
|
Cylinder block |
||||
|
ThreeBond |
||||
|
Oil pan |
Oil pan sealing face |
|||
|
1207C |
||||
1 — 19

SERVICE STANDARDS
1 — 20

TOOLS LIST
1.General Tools ····················································································· 1 -22
2.Special Tools······················································································· 1 -23
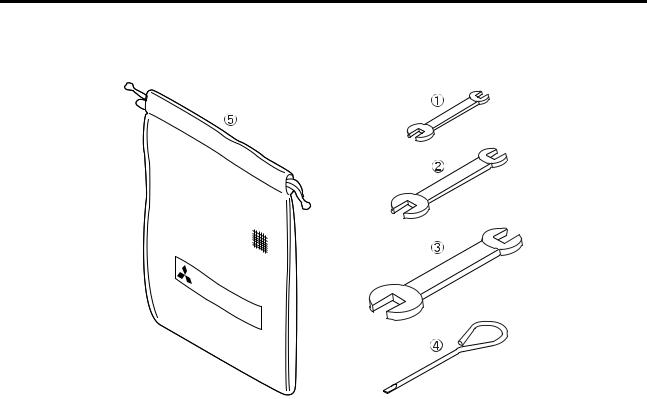
TOOLS LIST
1. General Tools
|
No. |
Description |
Part number |
Remarks |
|
― |
Tool set |
MM413-900 |
Consists of items to |
|
Spanner |
MK96008010 |
Width across flats [8×10 mm (0.31×0.39 in.)] |
|
|
Spanner |
MK96012014 |
Width across flats [12×14 mm (0.47×0.55 in.)] |
|
|
Spanner |
MK96017019 |
Width across flats [17×19 mm (0.67×0.75 in.)] |
|
|
Screwdriver |
MM300110 |
(-) |
|
|
Tool bag |
MM300783 |
||
1 — 22
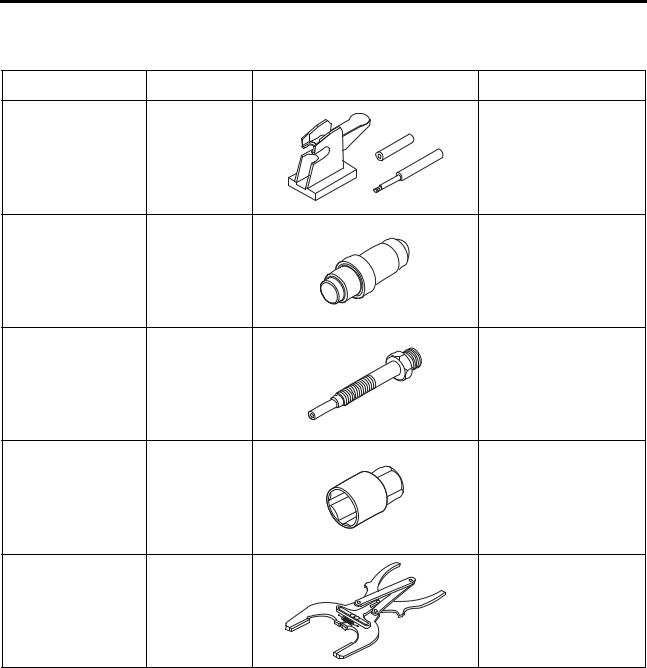
|
TOOLS LIST |
|||
|
2. Special Tools |
|||
|
Description |
Part number |
Shape |
Application |
|
Piston Pin |
31A91-00100 |
Piston pin |
|
|
Setting Tool |
removal / installation |
|
Camshaft Bushing |
ST332340 |
Punching / press-fitting of |
|
Installer |
front camshaft bushing |
|
Compression Gauge |
ST332270 |
Compression measuring |
|
Adapter |
|
Oil Pressure Switch |
MD998054 |
Oil pressure switch |
|
Socket Wrench |
removal / installation |
|
|
(26) |
|
Piston Ring Pliers |
31391-12900 |
Piston ring |
|
removal / installation |
1 — 23

TOOLS LIST
1 — 24

OVERHAUL TIMING
1.Identifying the Timing for Overhaul······················································ 1-26
2.Measuring the Compression Pressure ················································ 1-27

OVERHAUL TIMING
1. Identifying the Timing for Overhaul
Generally, when the compression pressure has dropped below the specified value, overhaul of the engine needs to be considered. Other parameters should also be considered in making the decision as to whether or not to overhaul the engine, such as engine oil consumption and blow-by gas volume.
Some of the phenomena that may suggest, but are not necessarily the criteria for, the need to overhaul the engine include reduced power, increased fuel consumption, oil pressure drop, difficulty in starting and higher noise level.
More specifically, reduction in compression pressure creates various types of phenomena in various combinations, and this is why it is difficult to make a correct decision. Typical phenomena include:
(a)Reduced power
(b)Increased fuel consumption
(c)Increased engine oil consumption
(d)Increased blow-by gas through the breather due to worn parts such as cylinder liners and pistons
(e)Increased blow-by gas due to poor seating of inlet / exhaust valves
(f)Poor starting
(g)Increased noise levels of various engine parts
(h)Abnormal color of exhaust gas after warm-up
Some of those listed above are directly related to the deterioration of the engine and some are not.
Items (b) and (f) are heavily influenced by fuel injection pump displacement, fuel injection timing, wearing of plungers, nozzle conditions, and conditions of electrical equipment such as battery and starter.
The most reliable criterion for engine overhaul is reduced compression pressure due to the wearing of cylinder liners and pistons [item (d)]. This should be combined with other items for comprehensive review to reach a rational conclusion.
1 — 26
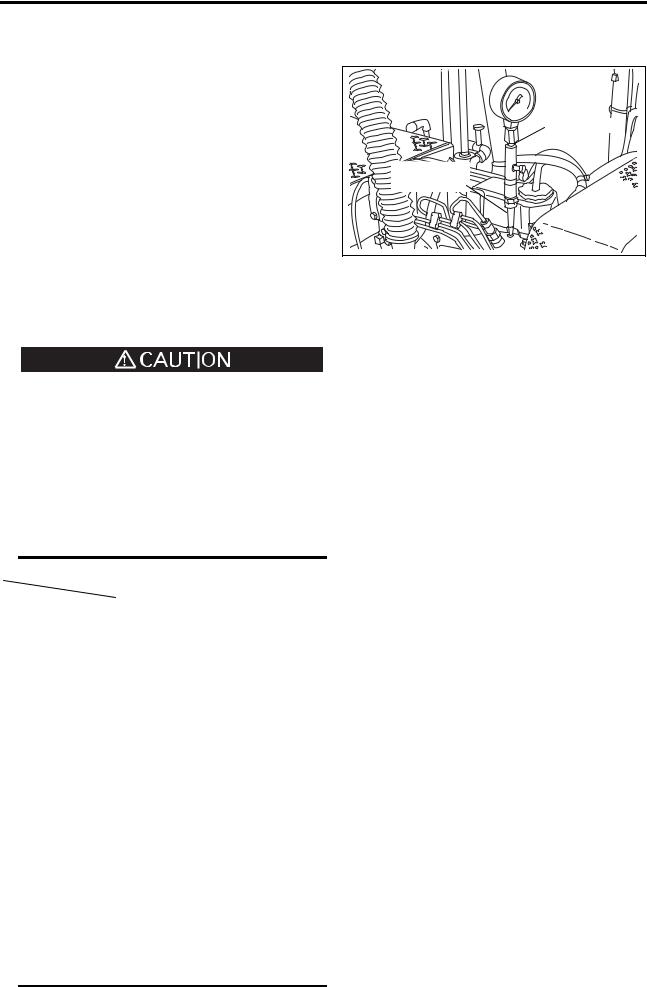
OVERHAUL TIMING
2. Measuring the Compression Pressure
(1) Move the control lever to STOP position.
(2) Remove the glow plugs from all cylinders. Install the special tool Compression Gauge Adapter and a compression gauge onto the cylinder being measured.
|
Special tool |
Part number |
|
Compression Gauge Adapter |
ST332270 |
(3) While cranking the engine with the starter, read the compression gauge. Note the reading at which the gauge needle stabilizes.
(4) If the measured value is at or below the limit, overhaul the engine.
(a)Measure all cylinders for compression pressure. Do not measure only one cylinder and make assumption about the other cylinders as this will lead to a wrong conclusion.
(b)Compression pressure varies depending on the engine speed. Keep the specified engine speed when measuring the compression pressure.
|
Standard value |
Limit |
|||
|
Engine speed |
290 min-1 |
|||
|
Compression |
2.9 MPa |
2.6 MPa |
||
|
(30 kgf/cm2) |
(27 kgf/cm2) |
|||
|
pressure |
[421 psi] |
[377 psi] |
||
|
Tolerable |
0.29 MPa |
|||
|
difference |
(3.0 kgf/cm2) |
|||
|
between |
[42 psi] |
|||
|
cylinders |
or less |
|||
Compression gauge
Compression gauge adapter
Measuring the compression pressure
It is important to regularly check the compression pressure so that you can tell the difference.
New or overhauled engines have slightly higher compression pressure.
The compression pressure settles to the standard value as the piston rings and valve seats fit in.
As wear progresses further, the compression pressure drops.
1 — 27

OVERHAUL TIMING
1 — 28

REMOVAL PREPARATIONS
1.Preparations ························································································ 1-30
1.1Removing the Electric Wiring ································································· 1-30
1.2Draining the Coolant············································································· 1-30
1.3Draining the Engine Oil ········································································· 1-30
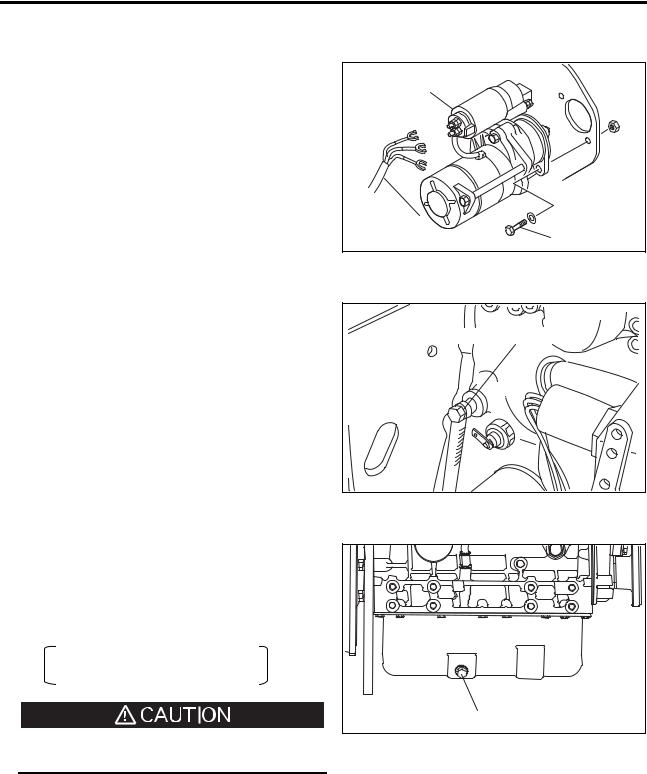
REMOVAL PREPARATIONS
1. Preparations
1.1Removing the Electric Wiring
Remove the wiring harnesses from the following equipment.
Before removal, attach mating tags etc. onto the terminals to aid reassembly.
StarterSwitches
Starter
|
Starter |
|
|
wiring |
Retaining bolt |
1.2Draining the Coolant
Loosen the coolant drain plug on the right-hand side face of the cylinder block to drain coolant from the engine.
1.3Draining the Engine Oil
Remove the engine oil drain plug from the oil pan to drain the engine oil.
Install and tighten the drain plug to the specified torque.
Oil pan capacity: 3.7 to 6.0 l
(1.0 to 1.6 U.S. gal)
Do not touch the engine oil which may be extremely hot as it can cause burns.
Removing the electric wiring
Coolant drain cock
|
Tightening torqe: |
|
|
34.3 to 44.1N m |
|
|
Drain piug |
(3.5 to 4.5kgf m) |
|
[25.3 to 32.5 lbf ft] |
Drain plug on the oil pan
1 — 30

ENGINE MAIN PARTS — DISASSEMBLY
1.Cylinder Head, Valve Mechanism························································ 2 — 2
1.1Removing the rocker shaft assembly ······················································· 2 — 3
1.2Disassembling the rocker shaft assembly ················································· 2 — 3
1.3Removing the cylinder head bolts ··························································· 2 — 3
1.4Removing the cylinder head assembly····················································· 2 — 4
1.5Removing the valves and valve springs ··················································· 2 — 4
1.6Removing the valve stem seals ······························································ 2 — 4
2.Flywheel, Timing Gear, Camshaft························································ 2 — 5
2.1Removing the flywheel·········································································· 2 — 7
2.2Removing the flywheel housing ······························································ 2 — 7
2.3Removing the rear plate ········································································ 2 — 8
2.4Removing the oil seal case ···································································· 2 — 8
2.5Removing the tappets ··········································································· 2 — 8
2.6Removing the crankshaft pulley ······························································ 2 — 8
2.7Removing the timing gear case ······························································ 2 — 9
2.8Measuring the timing gear backlash ························································ 2 — 9
2.9Removing the idler gear ······································································· 2 -10
2.10Removing the camshaft········································································ 2 -10
2.11Removing the fuel injection pump camshaft ············································· 2 -10
2.12Separating the gears from the shafts (as required)···································· 2 -10
2.13Removing the oil pump ·········································································2 -11
2.14Removing the front plate ·······································································2 -11
3.Cylinder Block, Crankshaft, Pistons, Oil Pan······································ 2 -12
3.1Removing the oil pan ··········································································· 2 -13
3.2Removing the oil strainer······································································ 2 -13
3.3Removing the connecting rod caps ························································ 2 -13
3.4Removing the pistons ·········································································· 2 -14
3.5Measuring the crankshaft end play························································· 2 -14
3.6Removing the main bearing caps ··························································· 2 -14
3.7Removing the crankshaft······································································ 2 -14
3.8Separating the piston from the connecting rod·········································· 2 -15
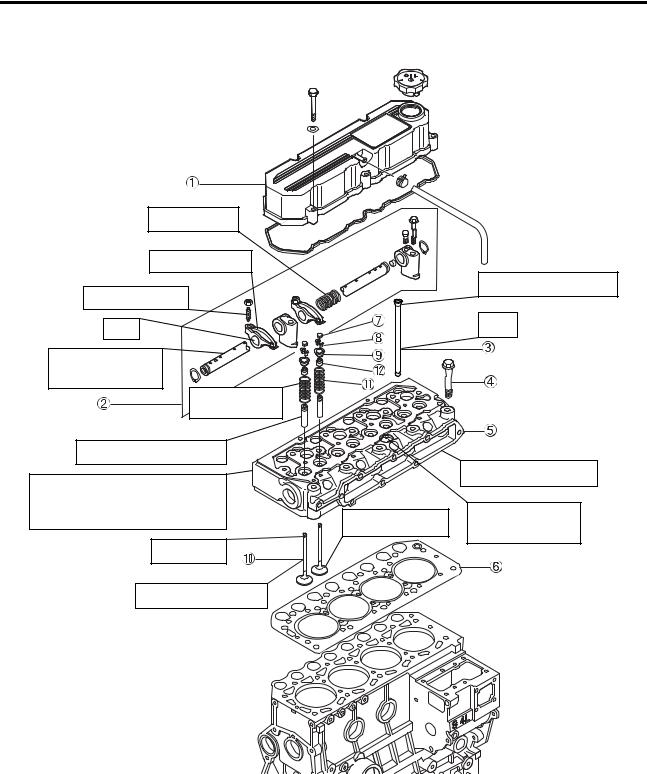
ENGINE MAIN PARTS — DISASSEMBLY
1. Cylinder Head, Valve Mechanism
Spring fatigue
Clogged oil hole
Damaged threads
Wear
Worn rocker shaft,
Clogged oil hole
Spring fatigue, damage
Valve guide wear, damage
Cracks, Damage, Coolant leakage,
Oil leakage, Scale formation,
Gasket, Carbon deposit
Dent, Wear
Stepped wear, Damage
End face wear, damage
Bend
|
Bottom face distortion |
|
|
Wear, |
Valve seat contact, |
|
Valve face contact |
damage, wear |
Disassembly of cylinder head and valve mechanism
|
<Disassembly sequence> |
||
|
Rocker cover |
Cylinder head |
Retainer |
|
Rocker shaft assembly |
Cylinder head gasket |
Valve |
|
Push rod |
Valve cap |
Valve spring |
|
Cylinder head bolt |
Valve lock |
Valve stem seal |
2 — 2
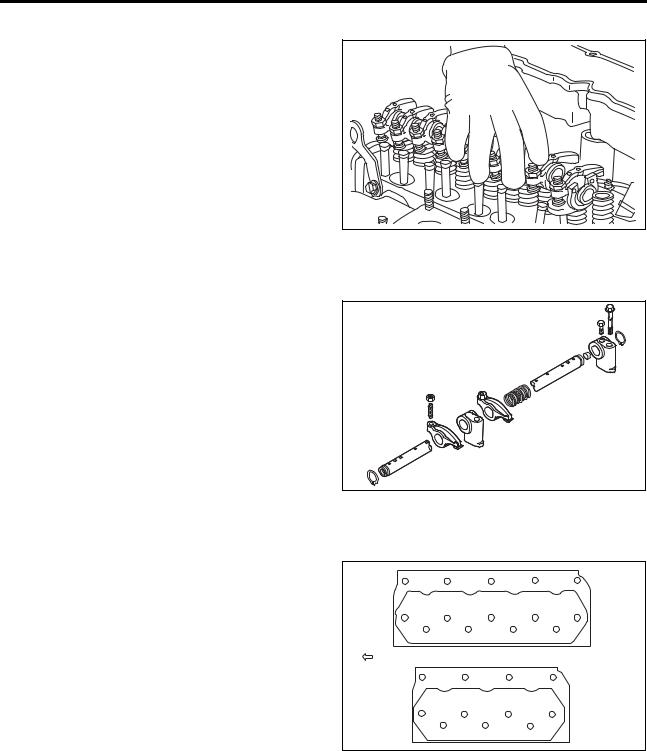
ENGINE MAIN PARTS — DISASSEMBLY
1.1 Removing the rocker shaft assembly
(1) Loosen the rocker stay bolts. Remove the rocker shaft assembly together with the rocker stay bolts.
(2) Remove the valve caps.
(3) Keep the rocker shaft assembly with the rocker stay bolts.
Removing the rocker shaft assembly
1.2Disassembling the rocker shaft assembly
In the course of disassembly, place removed valve rockers as well as the other parts neatly in the order of disassembly so that they can be reassembled back onto their original locations. Doing so, original clearances between the valve rockers and the rocker shaft is restored upon reassembly.
1.3Removing the cylinder head bolts
Loosen the cylinder head bolts in the order of the numbers illustrated. Do not loosen one bolt
completely before moving to the next bolt. Loosen the bolts in a couple of steps.
Note: Before removing the cylinder head bolts, check the cylinder head components for any fault. If faulty, check the bolts for tighteness with a torque wrench.
Disassembling the rocker shaft assembly
|
1 |
7 |
9 |
6 |
4 |
|
|
3 |
5 |
10 |
8 |
2 S4L, |
|
|
11 |
S4L2 |
||||
|
12 |
14 |
13 |
|||
|
Front of engine |
|||||
|
1 |
5 |
7 |
2 |
||
|
3 |
8 |
6 |
4 S3L,S3L2 |
||
|
10 |
11 |
9 |
Tightening order for cylinder head bolts
2 — 3
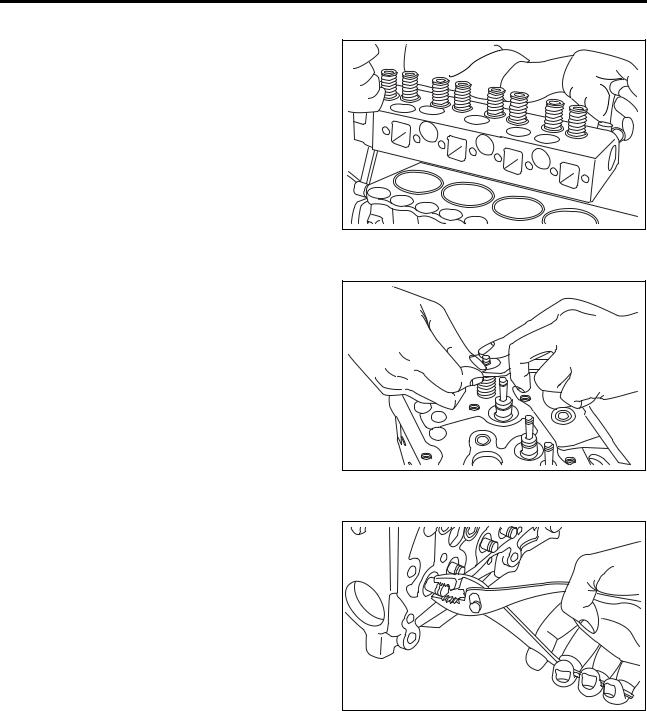
ENGINE MAIN PARTS — DISASSEMBLY
1.4 Removing the cylinder head assembly
Remove the cylinder head assembly by lifting it straight up.
Note:If the bonding of the cylinder head gasket prevents the head assembly from being separated from the cylinder block, tap the cylinder head side face on a relatively thick portion with a plastic hammer.
Removing the cylinder head assembly
1.5 Removing the valves and valve springs
(1)Remove the valve caps and locks by compressing the springs using a valve lifter.
(2)Remove the retainers, valve springs and valves. Note:If the valves are reusable, mark them so that
they can be reassembled back onto their original locations. This will ensure that the mated pairs of valves and their seats are maintained.
1.6 Removing the valve stem seals
Remove the valve stem seals by holding each of them with a pair of pliers.
Note:Replace the old valve stem seals with new parts upon reassembly.
Removing the valve spring
Removing the valve stem seal
2 — 4
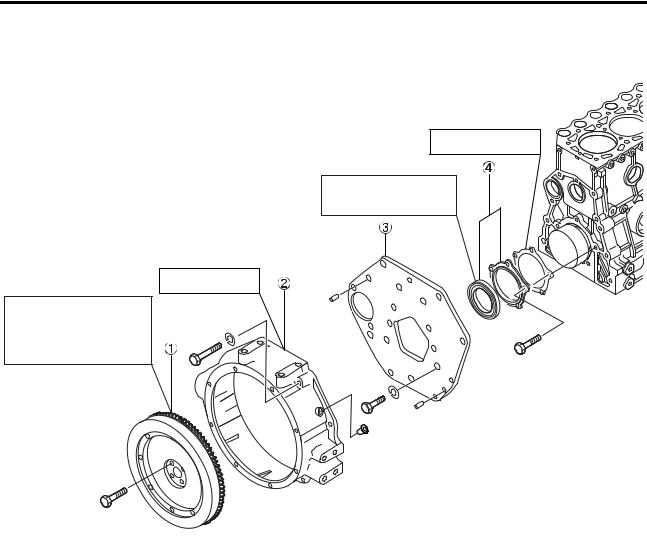
ENGINE MAIN PARTS — DISASSEMBLY
2. Flywheel, Timing Gear, Camshaft
Flywheel end of engine
Replace: Gasket
Oil seal wear, damage, deterioration
Cracks, Damage
Frictional surface streak, stepped wear, cracks; Ring gear damage, abnormal wear
|
Disassembly of flywheel |
|
|
<Disassembly sequence> |
|
|
Flywheel |
Rear plate |
|
Flywheel housing |
Oil seal case, Oil seal |
2 — 5